Welcome to the ultimate guide to underground rainwater harvesting systems, where we’ll show you how to save water and protect the environment. With increasing water scarcity and growing concerns about climate change, it’s more important than ever to find sustainable solutions for our water needs.
Rainwater harvesting is a simple yet effective way to make the most of this valuable resource. By collecting rainwater from rooftops and directing it into underground storage tanks, you can reduce your reliance on mains water and lower your water bills. But it doesn’t stop there. Underground rainwater harvesting systems also help to prevent flooding, reduce stormwater runoff, and replenish groundwater reserves.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about underground rainwater harvesting systems. We’ll discuss the benefits, types of systems, installation process, and maintenance tips. We’ll also explore how to integrate these systems into your existing infrastructure and maximize your water savings.
So, whether you’re a homeowner looking to go green or a business owner seeking sustainable solutions, this guide is your go-to resource for all things underground rainwater harvesting. Let’s dive in and start making a positive impact on our environment, one raindrop at a time.

1. Benefits of Underground Rainwater Harvesting
Underground rainwater harvesting systems offer numerous benefits, making them an excellent choice for sustainable water management. Some of the key advantages include:
- Space Efficiency: By storing water underground, these systems free up valuable surface space, making them ideal for urban areas or properties with limited space.
- Protection from Contamination: Being buried underground, the water is shielded from sunlight, reducing the risk of algae growth and contamination.
- Aesthetic Appeal: With the system hidden underground, it does not interfere with the landscaping or aesthetic appearance of your property.
- Sustainable Water Supply: Harvested rainwater can be used for irrigation, flushing toilets, laundry, and even potable use with proper filtration, reducing reliance on municipal water.
- Flood Mitigation: These systems help manage stormwater runoff, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion on your property.
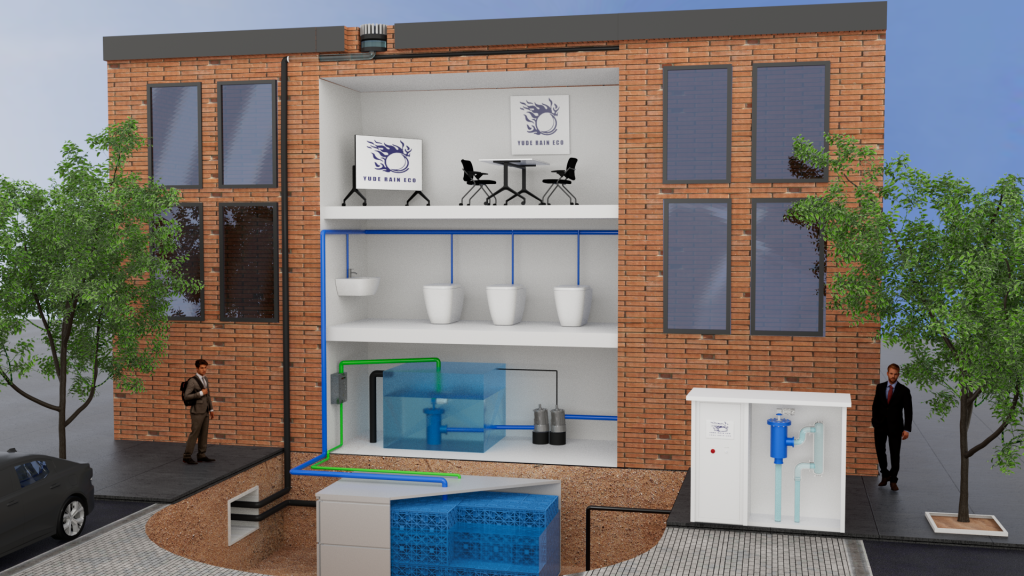
2. How Underground Rainwater Harvesting Systems Work
Underground rainwater harvesting systems operate by collecting rainwater from surfaces like rooftops, filtering it, and then storing it in underground tanks for later use. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the process:
- Collection: Rainwater is captured from roof surfaces via gutters and downspouts.
- Pre-filtration: The collected water passes through filters that remove leaves, debris, and other contaminants.
- Storage: Filtered water is directed into underground tanks made of durable materials such as polyethylene or concrete.
- Distribution: When needed, the stored water is pumped from the underground tank to where it is required, such as garden irrigation systems or household plumbing.
- Overflow Management: Any excess rainwater during heavy rainfall is safely diverted to a soakaway or drainage system to prevent flooding.
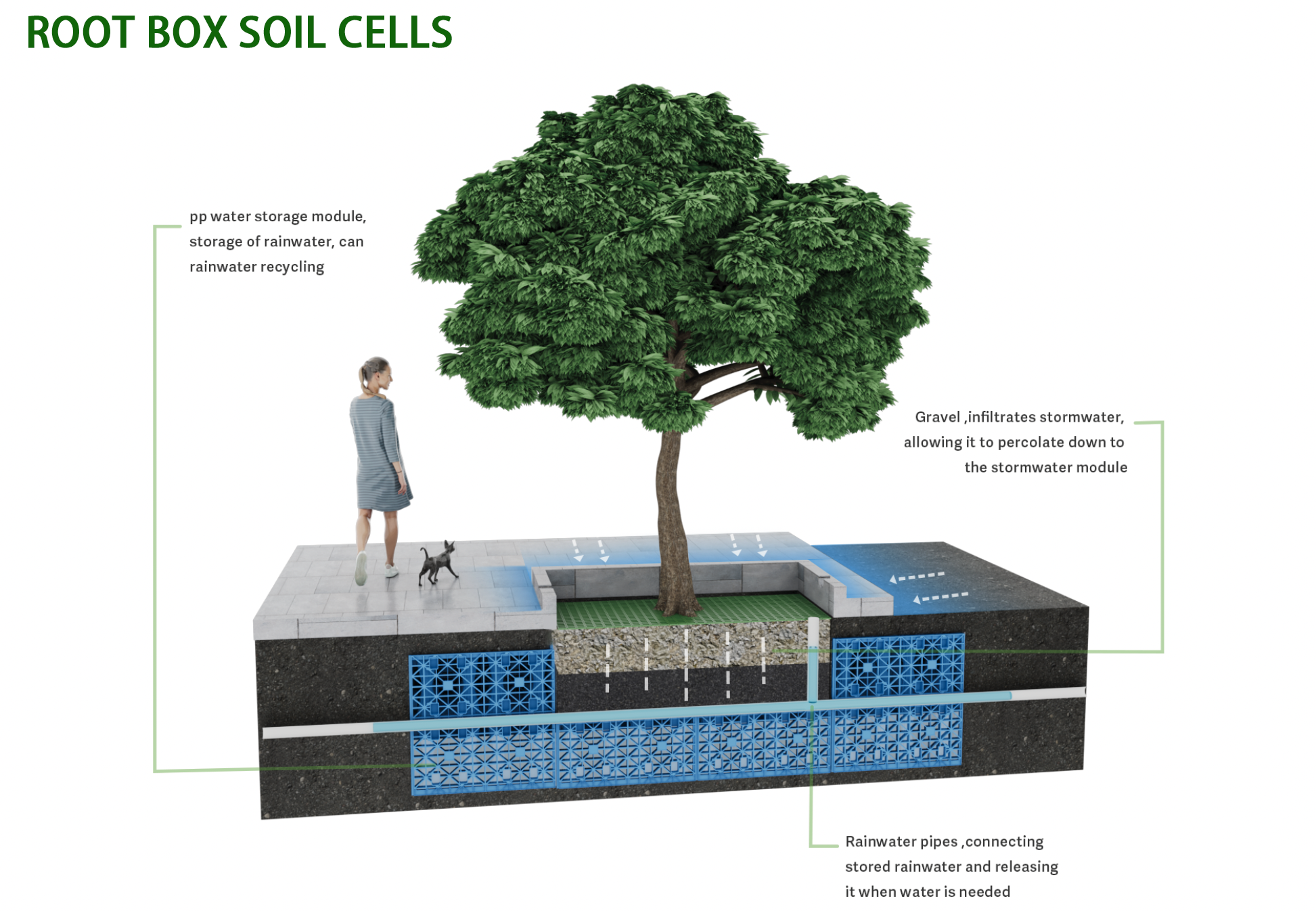
3. Components of an Underground Rainwater Harvesting System
An underground rainwater harvesting system consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring the system’s efficiency and effectiveness:
- Catchment Area: Typically the roof of a building, where rainwater is initially collected.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Channels that direct rainwater from the roof to the storage system.
- First-Flush Diverter: A device that removes the first portion of rainwater, which may contain debris and contaminants.
- Filters: Systems to clean the water before it enters the storage tank, ensuring that only clean water is stored.
- Underground Storage Tank (Underground Rainwater Attenuation): A tank made from materials like polyethylene, concrete, or fiberglass, where the filtered water is stored.
- Pump and Control System: Pumps water from the tank to the desired location, with controls to manage flow and pressure.
- Overflow System: A mechanism to safely handle excess water during heavy rain events, typically diverting it to a soakaway or stormwater drain.
4. Designing and Planning Your Underground Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Designing an underground rainwater harvesting system involves careful planning to ensure it meets your needs and complies with local regulations. Consider the following steps:
- Assess Water Needs: Determine the volume of water you wish to harvest and store based on your household or property requirements.
- Site Selection: Choose an appropriate location for the underground tank, considering factors like soil type, groundwater levels, and accessibility.
- Tank Sizing: Calculate the size of the storage tank based on the roof area, average rainfall, and intended water usage.
- System Layout: Plan the layout of the collection, filtration, storage, and distribution components, ensuring efficient flow and accessibility for maintenance.
- Compliance: Check local regulations and obtain any necessary permits for installing the system.
Ask Yude Rain Eco today | What size underground rainwater harvesting system does your building need?
5. Installation and Maintenance of Underground Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to the long-term success of your underground rainwater harvesting system:
Installation:
- Excavation: Digging the site to the required depth for the tank.
- Tank Placement: Positioning and securing the underground tank.
- Connection: Linking the tank to the collection and distribution systems.
- Backfilling: Covering the tank with soil and restoring the landscape.
- System Testing: Checking for leaks and ensuring all components function correctly.
Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Check gutters, filters, and the tank for debris, blockages, and signs of wear.
- Cleaning: Periodically clean the tank and filters to maintain water quality.
- Pump Servicing: Ensure the pump is functioning efficiently and replace parts as needed.
- Winterizing: In colder climates, take steps to protect the system from freezing.
6. Regulations and Permits for Underground Rainwater Harvesting
Compliance with local regulations is essential when installing an underground rainwater harvesting system. Here are key considerations:
- Permits: Depending on your location, you may need permits for excavation, plumbing, and water storage.
- Building Codes: Ensure the system meets local building codes, including tank placement, structural integrity, and water safety standards.
- Water Rights: In some regions, there are restrictions on rainwater harvesting due to water rights laws. Check with local authorities to understand any limitations.
- Environmental Impact: Some areas require environmental impact assessments before installation, especially if the system may affect local groundwater or ecosystems.
- Health and Safety: Regulations may dictate the quality of stored water, especially if it’s intended for potable use.
7. Tips for Maximizing the Efficiency of Your Underground Rainwater Harvesting System
To ensure that your underground rainwater harvesting system operates at its full potential, there are several strategies and best practices you can implement. By following these tips, you can maximize the efficiency of your system and get the most out of your investment in water conservation.
Proper System Design and Sizing
One of the most important factors in maximizing efficiency is proper system design and sizing. It’s crucial to carefully assess your water needs and the available catchment area to determine the appropriate size and capacity of your underground storage tank. Oversizing the tank can lead to inefficient use of space and resources, while undersizing can result in insufficient water storage and potential water shortages. Accurately calculating your needs and matching them with the correct tank size ensures that you maximize storage without wasting resources.
Selection and Maintenance of the Filtration System
The selection and upkeep of your filtration system are critical to maintaining water quality and system longevity. Properly filtered rainwater is free of debris and contaminants, which prevents clogging and reduces wear on your pump and distribution system. Regularly cleaning or replacing filters as needed keeps the system running efficiently and maintains the quality of the stored water. A well-maintained filtration system not only protects the equipment but also ensures that the water you collect remains safe for its intended uses.
Incorporate Water-Efficient Appliances and Fixtures
To further enhance the efficiency of your underground rainwater harvesting system, consider integrating water-efficient appliances and fixtures into your plumbing. Low-flow toilets, showerheads, and faucets can significantly reduce overall water consumption, allowing you to stretch your stored rainwater further. By reducing demand on your water supply, these fixtures help you make the most of the harvested rainwater, ensuring that your conservation efforts have a greater impact.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Routine monitoring and maintenance are essential to keeping your underground rainwater harvesting system functioning at its best. Regular checks for leaks, tank inspections, and assessments of the system’s components can identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Ensuring that the pump and distribution system are operating correctly is vital for the consistent delivery of stored rainwater. By staying proactive with maintenance, you can extend the lifespan of your system and guarantee that it continues to provide reliable water savings for years to come.
By focusing on these key areas—design, filtration, efficient appliances, and regular maintenance—you can maximize the efficiency of your underground rainwater harvesting system. These strategies not only improve system performance but also ensure that you achieve the greatest possible benefit from your investment in sustainable water management.
8. Examples and Case Studies of Successful Underground Rainwater Harvesting Projects
To illustrate the real-world benefits and applications of underground rainwater harvesting systems, let’s explore a few examples of successful projects from around the world.
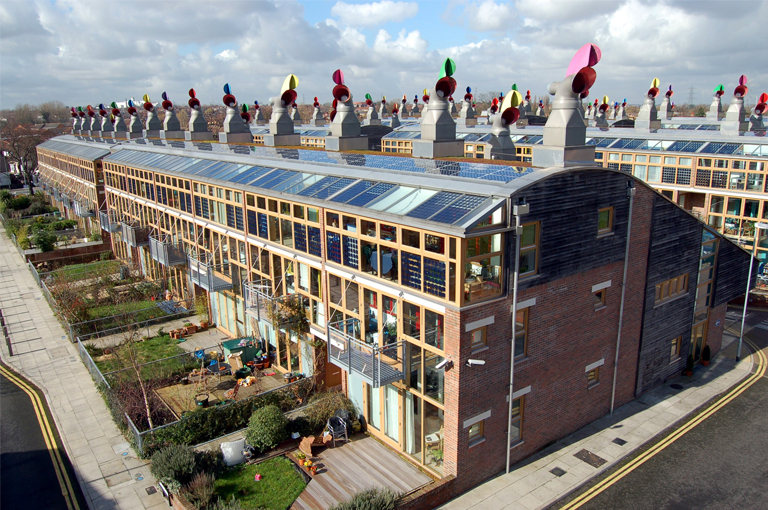

- Beddington Zero Energy Development (BedZED), London, UK
One notable example is the Beddington Zero Energy Development (BedZED) in London, UK. This innovative eco-village features an extensive underground rainwater harvesting system that collects and stores rainwater from the roofs of its residential and commercial buildings. The stored water is then used for toilet flushing, laundry, and landscape irrigation, reducing the development’s reliance on municipal water supplies by up to 50%.
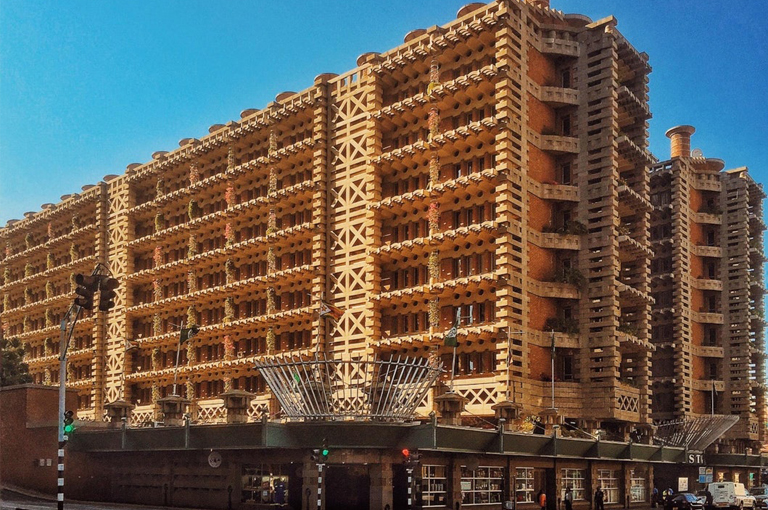

- Eastgate Centre, Harare, Zimbabwe
Another impressive case study is the Eastgate Centre in Harare, Zimbabwe. This commercial building, designed by architect Mick Pearce, incorporates an underground rainwater harvesting system that collects and stores up to 40,000 liters of water. The stored rainwater is used for the building’s cooling system, significantly reducing the building’s energy consumption and environmental impact.
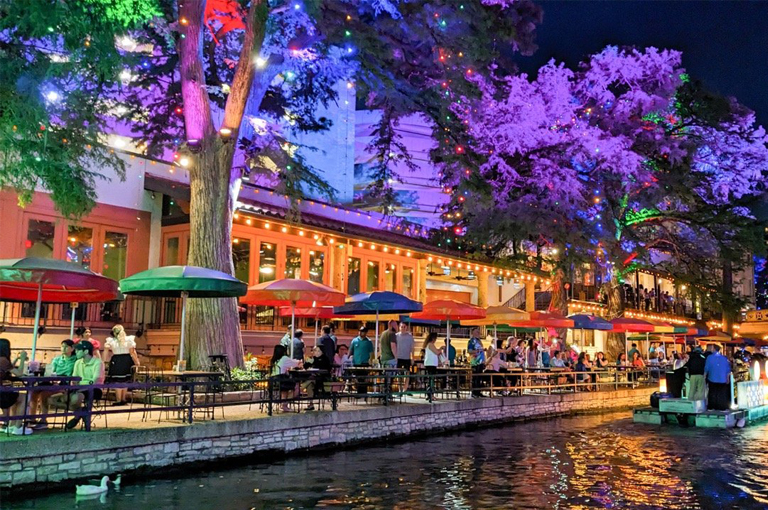

- San Antonio, Texas, USA
In the United States, the city of San Antonio, Texas, has been a leader in promoting the use of underground rainwater harvesting systems. The city’s “Rain to Drain” program provides incentives and rebates to homeowners and businesses who install these systems, with the goal of reducing the strain on the city’s water infrastructure and promoting sustainable water management practices.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of underground rainwater harvesting systems in a variety of settings, from residential developments to commercial buildings and even at the municipal level. By implementing these systems, communities and individuals can not only save water and reduce their environmental footprint but also contribute to the long-term sustainability of our precious water resources.
9. Conclusion: The Importance of Underground Rainwater Harvesting for Water Conservation and Environmental Protection
Underground rainwater harvesting is a powerful tool for conserving water and protecting the environment. By capturing and storing rainwater underground, these systems provide a sustainable water source that reduces demand on municipal supplies, mitigates flooding, and supports healthy landscapes. As we face increasing water scarcity and environmental challenges, adopting underground rainwater harvesting systems is a proactive step toward ensuring a resilient and sustainable future.
Call to Action
Yude Rain Eco are committed to helping you design and implement efficient underground rainwater harvesting systems tailored to your needs. Our expert team will guide you through the entire process, from planning and installation to maintenance, ensuring your system operates at peak efficiency.
Contact us today to learn how our solutions can help you conserve water, protect the environment, and achieve long-term sustainability.
Reach out to our specialists to start your journey toward responsible rainwater management.
* Underground rainwater harvesting system and the recommended maintenance frequency for each part.
| Component | Function | Recommended Maintenance Frequency |
| Catchment Area (Roof) | Collects rainwater | Inspect and clean annually |
| Gutters and Downspouts | Direct rainwater to the storage system | Inspect and clean every 3-6 months |
| First-Flush Diverter | Removes initial debris-laden rainwater | Inspect and clean every 6 months |
| Filters (Pre-filtration) | Removes debris and contaminants from water | Inspect and clean every 3-6 months |
| Underground Storage Tank | Stores filtered rainwater | Inspect for leaks and sediment annually |
| Pump and Control System | Pumps water from the tank to usage points | Inspect and service every 6-12 months |
| Overflow System | Manages excess water during heavy rainfall | Inspect and clean annually |
| Soakaway or Infiltration Trenches | Allows excess water to percolate into the ground | Inspect and maintain annually |
| Pipes and Connections | Distribute water from the tank to usage points | Inspect for leaks and blockages annually |
| Water Quality Testing (if potable use) | Ensures stored water is safe for drinking | Test water quality every 6 months |
FAQ: Underground Rainwater Harvesting Systems
1. How much does it cost to install an underground rainwater harvesting system?
The cost of installation can vary widely depending on the size of the system, the type of tank, the complexity of the plumbing, and local labor costs. On average, a residential system might cost anywhere from a few thousand to several tens of thousands of dollars. It’s important to get multiple quotes and consider long-term savings on water bills when evaluating the cost.
2. How long does it take to install an underground rainwater harvesting system?
The installation time can vary depending on the complexity of the system and the size of the tank. Typically, it can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, including time for excavation, tank placement, and connecting the system. Factors like weather conditions and site accessibility can also affect the timeline.
3. Can an underground rainwater harvesting system be installed in any type of soil?
Most soils can accommodate underground tanks, but the type of soil can influence the installation process. For example, clay soils may require additional measures for drainage, while sandy soils might need reinforcement to prevent collapse during excavation. A professional site assessment is recommended to determine the best approach.
4. What happens if the tank overflows during heavy rainfall?
Underground rainwater harvesting systems are typically designed with an overflow mechanism that diverts excess water to a soakaway or drainage system. This prevents flooding around the tank and ensures that the surrounding area remains safe. Regular maintenance of the overflow system is crucial to ensure it functions properly during heavy rain.
5. Is there a risk of contamination from the tank being underground?
When properly installed and maintained, underground tanks are designed to minimize the risk of contamination. The tank should be made of durable, non-toxic materials, and all joints and connections should be sealed to prevent infiltration from the surrounding soil. Regular inspection and maintenance are important to ensure the integrity of the system.
6. How do I know if my property is suitable for an underground rainwater harvesting system?
Several factors determine the suitability of your property, including the amount of rainfall in your area, the size of your roof (or other catchment areas), the soil type, and available space for excavation. Consulting with a professional can help assess these factors and determine if an underground system is a good fit for your property.
7. Can I retrofit an underground rainwater harvesting system to an existing building?
Yes, it is possible to retrofit an underground rainwater harvesting system to an existing building. However, the feasibility and cost will depend on factors such as available space for the tank, existing plumbing, and site access for excavation. It’s advisable to consult with a specialist who can evaluate your property and provide recommendations.
8. How much maintenance does the system require after installation?
Maintenance requirements are generally low but important. Regular checks are needed to clean gutters and filters, inspect the tank and pump, and ensure the overflow system is clear. The frequency of maintenance tasks will depend on your environment (e.g., nearby trees can increase debris) and system usage.
9. What happens if the underground tank leaks?
If a leak occurs, it should be addressed as soon as possible to prevent water loss and potential damage to the surrounding area. Depending on the severity of the leak, repairs might involve sealing cracks or replacing parts of the tank. Regular inspections can help catch leaks early before they become serious issues.
10. Can I use the system during the winter?
Yes, underground rainwater harvesting systems can be used during the winter. However, in regions with freezing temperatures, it’s essential to winterize the system to prevent pipes from freezing and to protect the pump. Insulating exposed pipes and ensuring the tank is buried below the frost line are common practices for winterizing.
11. How do I deal with sediment buildup in the tank?
Over time, some sediment may accumulate at the bottom of the tank. Regular inspection can help you monitor this. If sediment buildup becomes significant, the tank may need to be drained and cleaned. Installing a pre-tank filter can reduce the amount of sediment that enters the tank.
12. Will the system increase the value of my property?
In many cases, installing a rainwater harvesting system can increase the value of your property, especially in areas where water conservation is a priority. Potential buyers may see it as a valuable feature that reduces water bills and supports sustainable living practices.