Case Study: Guangzhou Rail Transit Line 14 Phase I – Lijiatang Station, Shengang Station, Taiping Station

Project Overview
Guangzhou Rail Transit Line 14 Phase I encompasses several key stations including Lijiatang, Shengang, and Taiping, which are critical components of Guangzhou’s expanding urban transit infrastructure. Given the substantial commuter traffic and the necessity for efficient, resilient infrastructure, Yude RainEco was commissioned to implement advanced water management solutions to ensure operational reliability and sustainability.
Objectives
The project aimed to address specific needs:
Enhanced Drainage Capacity: To manage high volumes of stormwater effectively and prevent flooding, which can disrupt transit operations and safety.
Sustainability: Integrate eco-friendly water management systems that align with the city’s broader environmental goals.
Long-term Durability and Low Maintenance: Implement solutions that require minimal maintenance while offering long-lasting performance, given the high-traffic nature of the transit system.
Yude RainEco’s Role
Yude RainEco’s involvement in the project was multifaceted, focusing on delivering top-tier water management systems that are both efficient and sustainable:
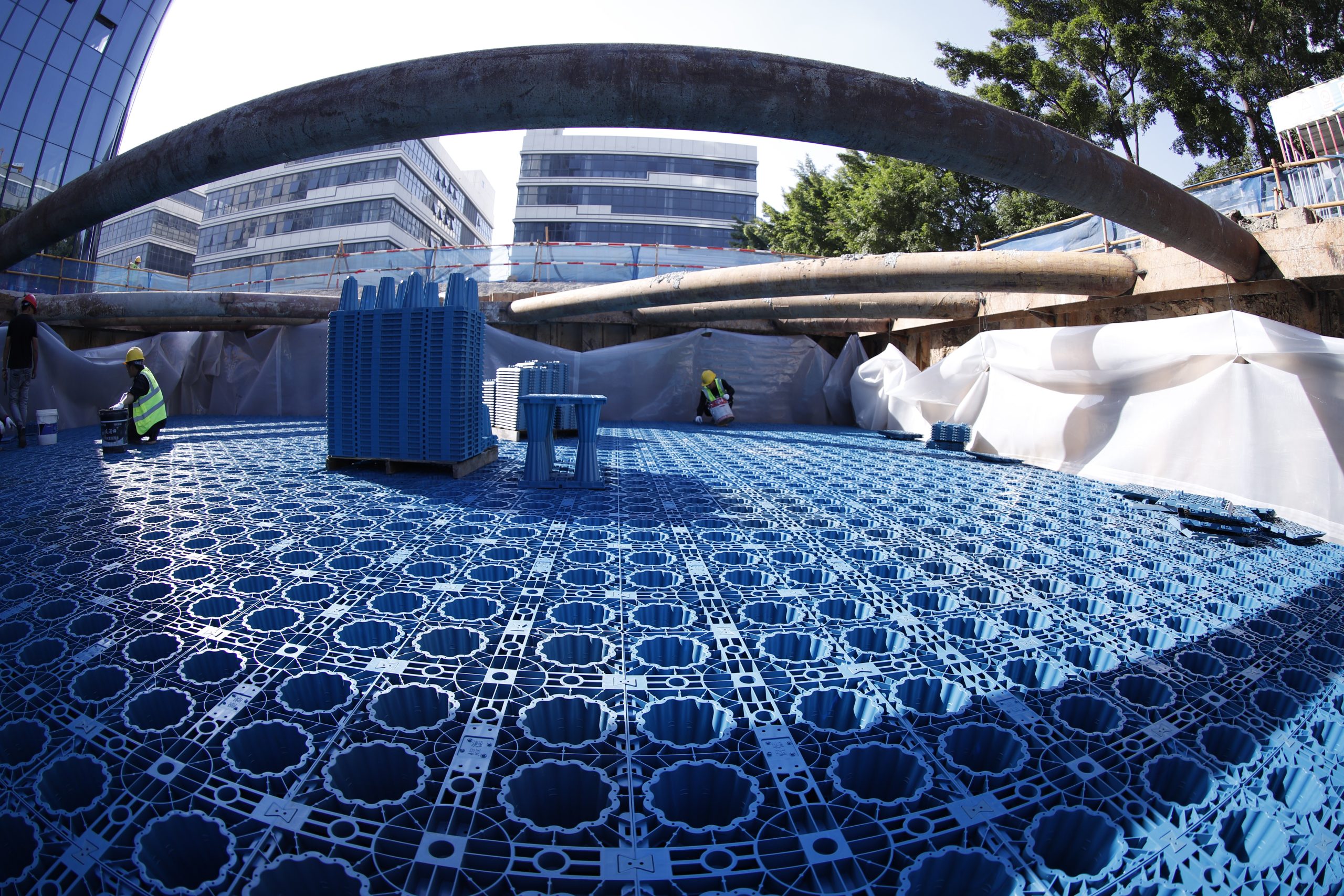
Siphon Drainage System:
A high-performance siphon drainage system was installed at each station to rapidly remove stormwater from platform areas and tracks. This system was designed to handle large volumes of water, crucial for preventing flooding during heavy rainfall, thus ensuring uninterrupted service and safety.
The design was integrated into the existing architecture of the stations, providing efficient drainage without compromising the structural integrity or aesthetic of the stations.
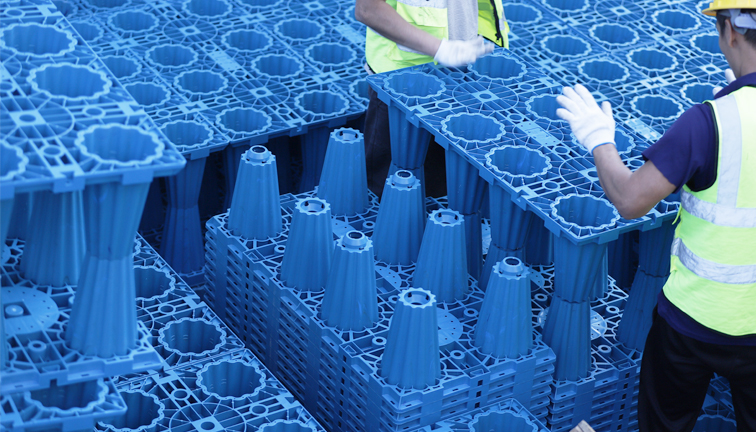
Modular Rainwater Harvesting System:
At each station, Yude RainEco implemented modular rainwater harvesting systems to collect and reuse rainwater for station maintenance tasks such as cleaning and landscaping. This not only reduced the stations’ dependence on municipal water supplies but also contributed to the sustainability targets of the transit authority.
Advanced Water Treatment:
The collected rainwater underwent treatment through advanced filtration systems to ensure it met safety standards for its intended use. This process is crucial for maintaining a clean and hygienic environment within the transit stations.
Results
Operational Efficiency: The effective management of stormwater significantly reduced the risk of delays and operational disruptions caused by adverse weather conditions.
Economic Benefits: Reduced reliance on municipal water systems decreased operational costs related to water usage.
Environmental Impact: By implementing sustainable water management practices, the stations contributed positively to the city’s environmental goals, enhancing the sustainability profile of the transit system.
Conclusion
The successful deployment of Yude RainEco’s water management solutions at Lijiatang, Shengang, and Taiping stations underlines the company’s expertise in adapting its technologies to meet the demands of complex urban infrastructure projects. This project demonstrates how innovative water management strategies can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of urban transit systems, making Yude RainEco a key player in supporting the growth of eco-friendly urban transportation networks.