Water Challenges in Germany
Urbanization and Impermeable Surfaces: Germany is a highly urbanized country with vast areas of impermeable surfaces, such as buildings, roads, and parking lots. This extensive urbanization reduces natural rainwater infiltration, increasing surface runoff. Consequently, cities face higher risks of urban flooding, particularly during heavy rainfall, putting immense pressure on urban drainage systems. According to a study by the German Environment Agency, urban areas have seen an increase of 15-20% in surface runoff over the past few decades due to increased impermeable surfaces.
Climate Change and Extreme Weather: With the impacts of climate change, Germany is experiencing more frequent extreme weather events, including more intense rainstorms and prolonged droughts. Heavy rainfall raises flood risks, while droughts lead to water scarcity, especially in summer months. Data from the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection (BMUV) indicates a 25% increase in extreme weather events over the last decade.
Pressure on Groundwater Resources: Despite Germany’s relatively abundant groundwater resources, high demand from agriculture, industry, and domestic use is putting these resources under pressure. In agricultural areas, excessive groundwater extraction may cause water levels to drop, potentially damaging ecosystems. The Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) reports that groundwater levels in some regions have decreased by as much as 15% in the past 20 years.
Water Challenges in Mexico
Water Scarcity: Mexico, particularly Mexico City, has long faced issues with water scarcity. The combination of a dense urban population and a dry climate exacerbates the imbalance between water supply and demand. Most of Mexico City’s water supply depends on distant sources, making water management more complex and costly. A report by Mexico’s National Water Commission (CONAGUA) indicates that about 40% of Mexico City’s water comes from external sources, significantly increasing the city’s vulnerability to water shortages.
Aging Infrastructure and Leakage: Mexico’s water supply infrastructure is severely aged in many areas, with problems such as pipe leaks and illegal water extraction leading to significant water loss, further exacerbating supply shortages. It is estimated that Mexico City alone loses approximately 30-40% of its water through leaks and illegal connections.
Overexploitation of Groundwater: Due to insufficient surface water supply, many regions rely on groundwater. Over-extraction of groundwater has led to declining water tables and land subsidence issues. According to CONAGUA, groundwater accounts for around 60% of the total water supply in Mexico, and in areas like Mexico City, over-extraction has caused land subsidence of up to 30 centimeters annually.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting for Germany and Mexico’s Water Scarcity
Rainwater harvesting systems offer significant benefits to both Germany and Mexico, and their rainfall levels are generally sufficient to support these systems. Below is an analysis of the specific benefits of rainwater harvesting for these countries, along with data on rainfall.
In Germany:
Reducing Flood Risk: In Germany, especially in urban areas, rainwater harvesting systems can effectively reduce surface runoff during heavy rainfall, easing the burden on urban drainage systems and preventing flooding. For example, the implementation of rainwater harvesting in Hamburg’s HafenCity has reduced stormwater runoff by up to 40%, according to local environmental reports.
Saving Water: With relatively high per capita water usage, Germany benefits from rainwater harvesting systems that provide an alternative source for non-potable water uses (such as toilet flushing, garden irrigation, and cleaning), thus reducing the demand for tap water and conserving freshwater resources. A study by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment shows that households with rainwater harvesting systems reduce their municipal water consumption by 30-50%.
Lowering Water Bills: By using rainwater instead of municipal water, businesses and households can lower their water bills. This is especially significant in areas where water prices are high; rainwater harvesting can lead to substantial cost savings. For example, some municipalities offer rebates on stormwater fees for properties with rainwater harvesting systems, encouraging more widespread adoption.
Environmental Protection: Reducing stormwater runoff helps protect natural waterways and groundwater resources, preventing soil erosion and pollution caused by excessive runoff. The German Environment Agency reports a 20% reduction in stormwater runoff pollution in areas with high rainwater harvesting adoption.
Supporting Sustainable Development: Rainwater harvesting systems are part of sustainable building design, helping enhance the ecological sustainability of buildings and communities, aligning with Germany’s stringent environmental standards. The German Green Building Council (DGNB) promotes rainwater harvesting as a key feature for sustainable building certification.
Rainfall Support in Germany:
- Rainfall Amount: Germany’s average annual rainfall is about 600 to 800 millimeters, depending on the region. Southern and western regions typically receive more rainfall; for example, Munich has an annual rainfall of about 950 millimeters, while Berlin receives about 600 millimeters.
- Feasibility of Rainwater Harvesting: Most regions in Germany have sufficient rainfall to support effective rainwater harvesting systems. The relatively even distribution of rainfall throughout the year enables rainwater harvesting systems to operate continuously, providing a reliable source of water for non-potable uses.
In Mexico:
Alleviating Water Scarcity: Mexico, particularly Mexico City, faces severe water scarcity issues. Rainwater harvesting systems can provide an alternative water source for households and communities, especially during dry seasons, alleviating water supply pressure. Initiatives like Isla Urbana have installed rainwater harvesting systems in over 20,000 homes, providing up to 40% of their annual water needs.
Reducing Supply Costs: By harvesting rainwater, reliance on municipal water supply is reduced, lowering water costs, especially in areas with tight water resources, unstable supply, or high water prices. The savings from using rainwater instead of municipal water can be substantial, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
Enhancing Water Resource Management: Rainwater harvesting systems can help Mexico improve water resource management, reduce the burden on water supply infrastructure, and cut maintenance costs, easing social and economic pressures caused by insufficient water supply.
Reducing Flood Risk: During the rainy season, especially in urban areas, rainwater harvesting systems can reduce surface runoff, lower flood risk, and protect infrastructure from flood damage. Mexico City has seen a 20% reduction in urban flooding incidents in areas with extensive rainwater harvesting systems, according to city planning reports.
Promoting Community Self-Sufficiency: Rainwater harvesting systems can enhance community self-sufficiency in water resources, particularly in remote or poorly serviced areas, improving the quality of life for residents.
Rainfall Support in Mexico:
- Rainfall Amount: Mexico’s average annual rainfall varies greatly, with rainfall mainly concentrated in the rainy season (typically from May to October). For instance, Mexico City’s average annual rainfall is about 700 millimeters, while other regions, such as the Yucatan Peninsula and Chiapas, can receive over 2,000 millimeters.
- Feasibility of Rainwater Harvesting: Although Mexico’s rainfall is seasonal, the heavy rains during the rainy season provide ample water to support effective rainwater harvesting systems. During periods of concentrated rainfall, rainwater harvesting systems can store enough water to be used during dry seasons.
Legal and Regulatory Support for Rainwater Harvesting in Germany and Mexico
Germany’s Legal and Regulatory Support for Rainwater Harvesting:
- Germany places great emphasis on sustainable development and environmental measures, including rainwater collection and utilization. The Federal Water Act (Wasserhaushaltsgesetz, WHG) explicitly encourages rainwater management and collection, particularly in reducing flood risk and protecting water resources.
- In some federal states, such as Bavaria (including Munich), local governments have established regulations requiring new buildings to include rainwater management measures. For example, many areas require new buildings to have retention and infiltration facilities to reduce stormwater runoff.
- Rainwater harvesting system installations are also incentivized by reducing stormwater fees, which are calculated based on the amount of rainwater discharged into the municipal drainage system. Thus, reducing rainwater discharge can directly lower costs.
Mexico’s Legal and Regulatory Support for Rainwater Harvesting:
- Mexico’s laws for promoting rainwater harvesting systems are relatively new, but in many cities, especially Mexico City, where water shortages are frequent, local governments are pushing for the application of rainwater harvesting systems.
- In 2014, Mexico City passed an environmental regulation requiring new buildings to consider installing rainwater harvesting systems during the permitting process, particularly on roofs and parking areas.
- The Mexican government also offers financial incentives, such as tax deductions and subsidies, to encourage individuals and businesses to install rainwater harvesting systems.
Examples of Buildings with Rainwater Harvesting Systems in Germany and Mexico
Examples of Buildings with Rainwater Harvesting Systems in Germany:
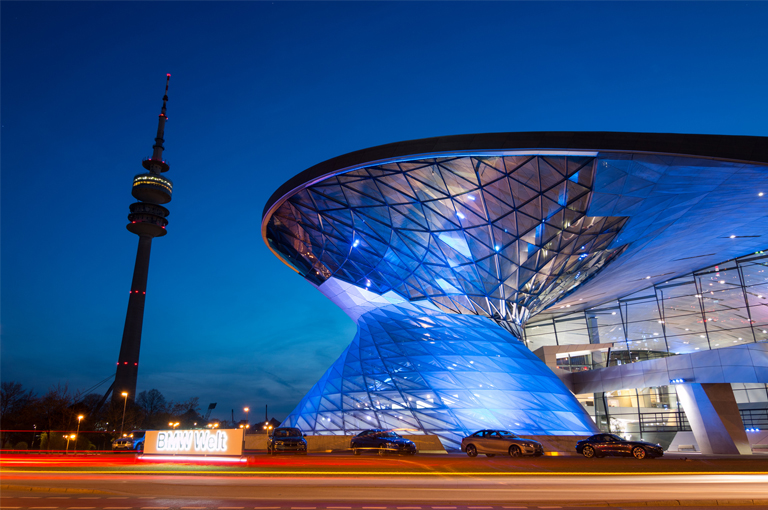

- Building Name: BMW Welt
- Location: Near Olympia Park, Munich
- Rainwater harvesting system details:
- System Size: The rainwater harvesting system at BMW Welt is very large and is designed to support the building’s sanitary water and irrigation needs. The collected rainwater is stored in an underground storage tank with a capacity of approximately 40,000 litres.
- Uses: The collected rainwater is mainly used for flushing toilets and irrigating the green areas around the building. In addition, the system helps to reduce the risk of flooding by reducing the pressure of rainwater runoff on the local drainage system.
- Environmental benefits: The system saves a significant amount of mains water resources each year and reduces pressure on municipal sewage treatment.
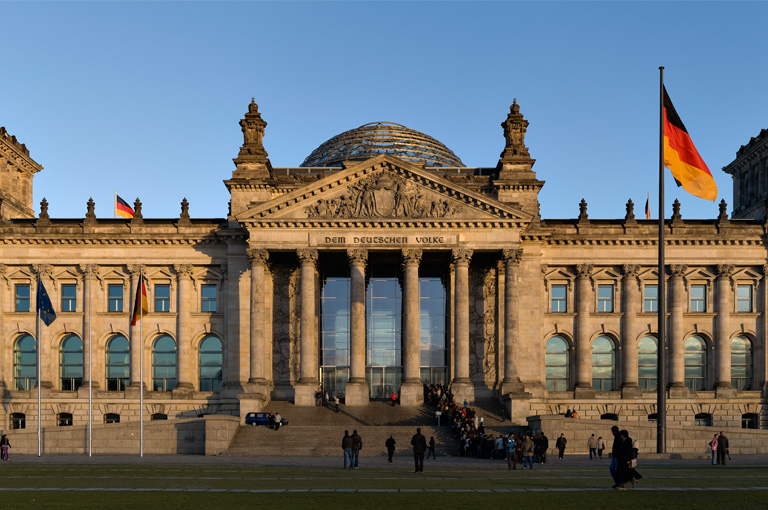

2. Reichstag Building (Berlin)
- Location: Berlin
- System Details: The rainwater harvesting system at the Reichstag is highly advanced, capable of collecting and storing about 2,000 cubic meters (2,000,000 liters) of rainwater.
- Usage: The harvested rainwater is mainly used for flushing toilets, cleaning, and irrigating green spaces around the building.
- Environmental Benefits: The system reduces the use of millions of liters of potable water annually, demonstrating Germany’s commitment to sustainability and environmental protection.
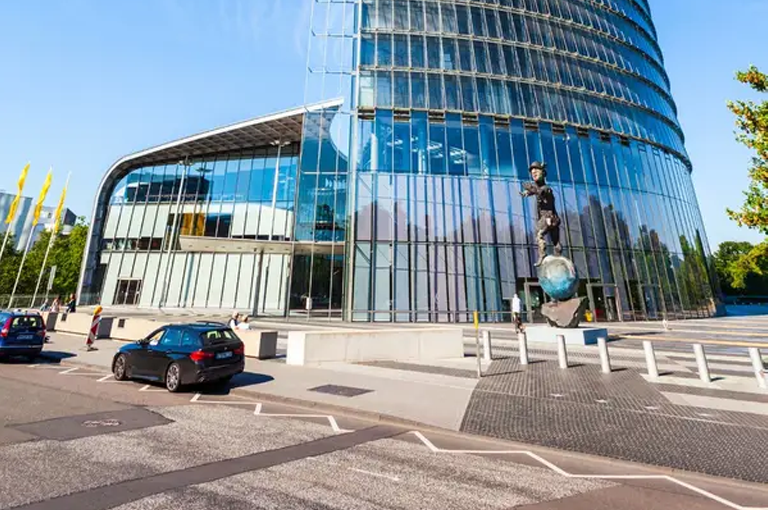

3. Deutsche Post Headquarters
- Location: Bonn
- System Details: The headquarters’ roof and parking areas feature a rainwater harvesting system with a total storage capacity of about 150,000 liters.
- Usage: The system is primarily used for non-potable applications, such as toilet flushing, external cleaning, and green space irrigation.
- Environmental Benefits: Through extensive rainwater collection and use, the building significantly reduces tap water consumption, showcasing the company’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
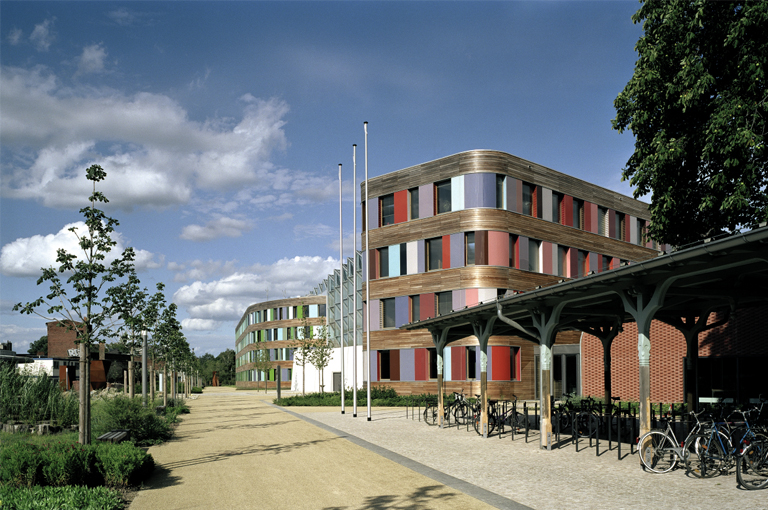

4. Federal Environment Agency Building
- Location: Dessau
- System Details: The building is equipped with a comprehensive rainwater harvesting and utilization system with a storage capacity of 30,000 liters.
- Usage: The system is used for restroom water supply and landscape irrigation, fully supporting the building’s environmental goals.
- Environmental Benefits: As a symbolic building for Germany’s environmental department, the rainwater harvesting system at the Federal Environment Agency Building plays a key role in water conservation and reducing urban drainage pressure.
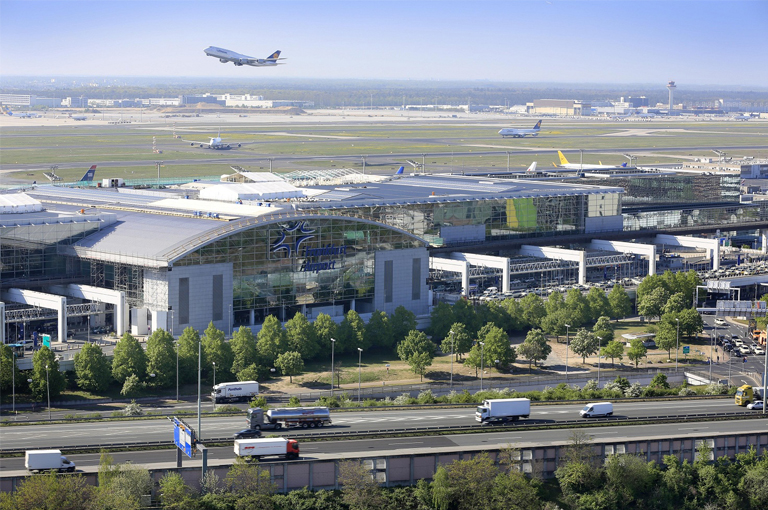

5. Frankfurt Airport Terminal 2
- Location: Frankfurt
- System Details: The airport’s Terminal 2 features a large rainwater harvesting system with a storage capacity of 100,000 liters.
- Usage: The collected rainwater is used for irrigation and toilet flushing within the terminal, significantly reducing the demand for municipal water.
- Environmental Benefits: By adopting rainwater harvesting systems in such large public facilities, Frankfurt Airport sets a benchmark in water resource management and environmental protection.
Residential neighbourhood case:
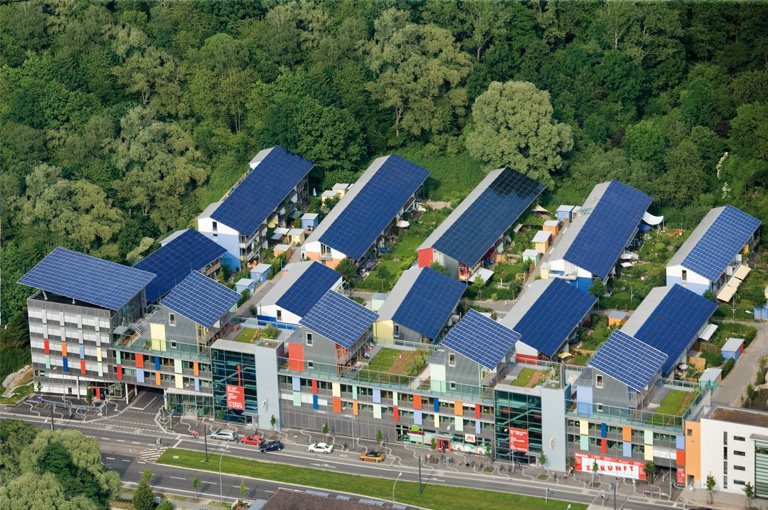

6. Solar Settlement in Freiburg
- Location: Freiburg
- System Details: Each building in this residential area is equipped with an independent rainwater harvesting system, typically with a storage capacity of about 3,000 to 5,000 liters.
- Usage: Rainwater is primarily used for garden irrigation and non-potable uses, such as car washing and cleaning.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar Settlement is a zero-energy housing area, and its rainwater harvesting systems further reduce the environmental footprint of residents.
7. A high-end residential area near Munich
- Location: Isarvorstadt,
- Rainwater harvesting system details:
- SYSTEM SIZE: Typical rainwater harvesting system sizes in these residential areas are typically between 10,000 and 20,000 litres, depending on the roof area and rainwater harvesting requirements of each property.
- Uses: Rainwater harvesting is mainly used for irrigating private gardens, cleaning terraces and flushing toilets. As the collected rainwater is not used for drinking, the system is relatively simple and requires only basic filtration equipment.
- Environmental benefits: Rainwater harvesting systems in residential areas significantly reduce the demand for municipal water and protect local drainage infrastructure by reducing runoff.
Examples of Buildings with Rainwater Harvesting Systems in Mexico
Commercial building example:
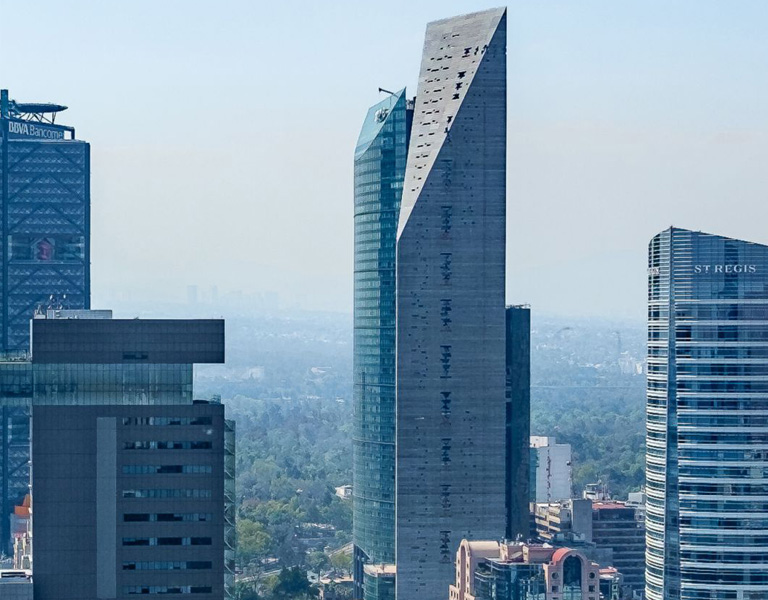

- Building name: Torre Reforma
- Location: Paseo de la Reforma, Mexico City
- Detail of rainwater harvesting system:
- System size:Torre Reforma’s rainwater harvesting system is designed to capture and store rainwater with a capacity of up to approximately 200,000 litres.
- Uses: The rainwater collected by the system is used for non-potable water needs inside the building, such as toilet flushing, cleaning and irrigating the internal plant walls. The rainwater undergoes a multi-stage filtration process to ensure that it is suitable for non-potable uses.
- Environmental benefits:By utilising rainwater, the building significantly reduces the use of mains water and demonstrates an example of a sustainable building that is less reliant on the municipal water supply system.
Residential neighbourhood case:
2. Location: a middle-income neighbourhood in the Tlalpan district of Mexico City
- Rainwater harvesting system detail:
- System size: Rainwater harvesting systems here typically have a storage capacity of between 5,000 and 10,000 litres, depending on the size of each house and the area of rainwater collection.
- Uses: The rainwater collected by these systems is mainly used for irrigating home gardens, flushing toilets and washing vehicles, helping households to reduce their water bills.
- Environmental benefits: By using the collected rainwater to partially replace tap water, the community significantly reduces their consumption of limited water resources and improves their quality of life in the face of water scarcity.
Conclusion
The rainfall in Germany and Mexico is sufficient to support the installation and operation of rainwater harvesting systems. These systems offer significant environmental, economic, and social benefits to both countries, helping to alleviate their respective water resource challenges. In Germany, stable rainfall throughout the year and a strong emphasis on environmental protection make rainwater harvesting an effective sustainable development measure. In Mexico, despite the seasonal nature of rainfall, rainwater harvesting provides a valuable alternative water source in times of scarcity and inadequate management.
Take Action with Yude Rain Eco! Facing water resource challenges? Yude Rain Eco offers innovative solutions! Contact us now to install a rainwater harvesting system and secure more water for the future.