Understanding Rainwater Attenuation Tanks
Rainwater attenuation is a critical process for managing stormwater runoff, capturing and storing rainwater to reduce flood risk and promote sustainable water practices. Rainwater attenuation crates, also known as stormwater attenuation crates or modular attenuation tanks, are essential components of this process. These underground modular structures provide a scalable and flexible solution to manage large volumes of stormwater effectively. By incorporating this method, urban areas can efficiently manage water resources, enhancing resilience against extreme weather events and contributing to overall sustainability.
The Importance of Sustainable Solutions
In today’s rapidly urbanizing world, sustainable solutions like rainwater attenuation are essential.
Rainwater attenuation systems support low-impact development (LID) strategies, enhancing urban resilience through decentralized water management. By mimicking natural infiltration and storage patterns, they reduce peak flows and help cities adapt to more frequent and intense rain events.
They play a vital role in mitigating the impacts of climate change, reducing environmental footprints, and ensuring long-term water security. Implementing rainwater attenuation systems is a proactive approach to addressing water management challenges and fostering sustainable urban development.
Benefits of Rainwater Attenuation Tanks
- Flood Prevention: By controlling the release of stormwater, it helps prevent urban flooding.
- Water Conservation: Collected rainwater can be reused for non-potable purposes, reducing demand on municipal water supplies.
- Environmental Protection: It supports natural hydrological cycles and minimizes soil erosion.
- Cost Savings: It reduces the need for extensive stormwater infrastructure, leading to financial savings for municipalities and property owners.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Modular rainwater attenuation crates can be easily scaled to match site-specific requirements, from small residential plots to large industrial zones.
- Compliance with SuDS Guidelines: In countries like the UK, attenuation systems help meet Sustainable Drainage System (SuDS) requirements for new developments.
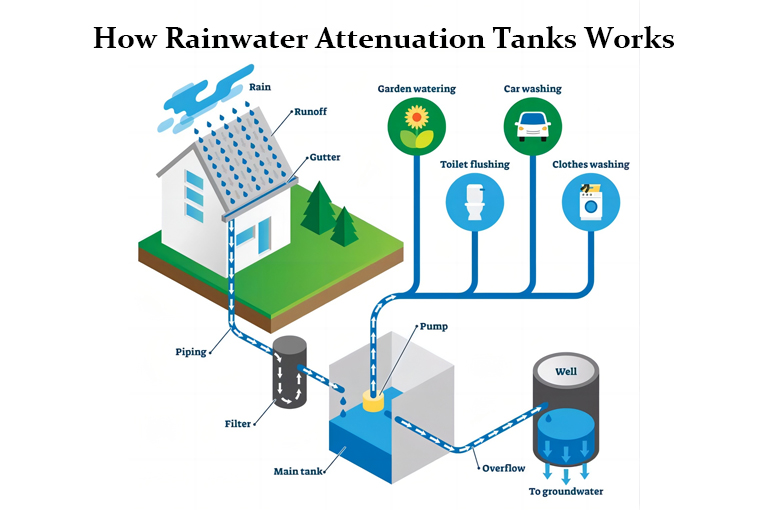
How Rainwater Attenuation Tanks Works? Step-by-Step
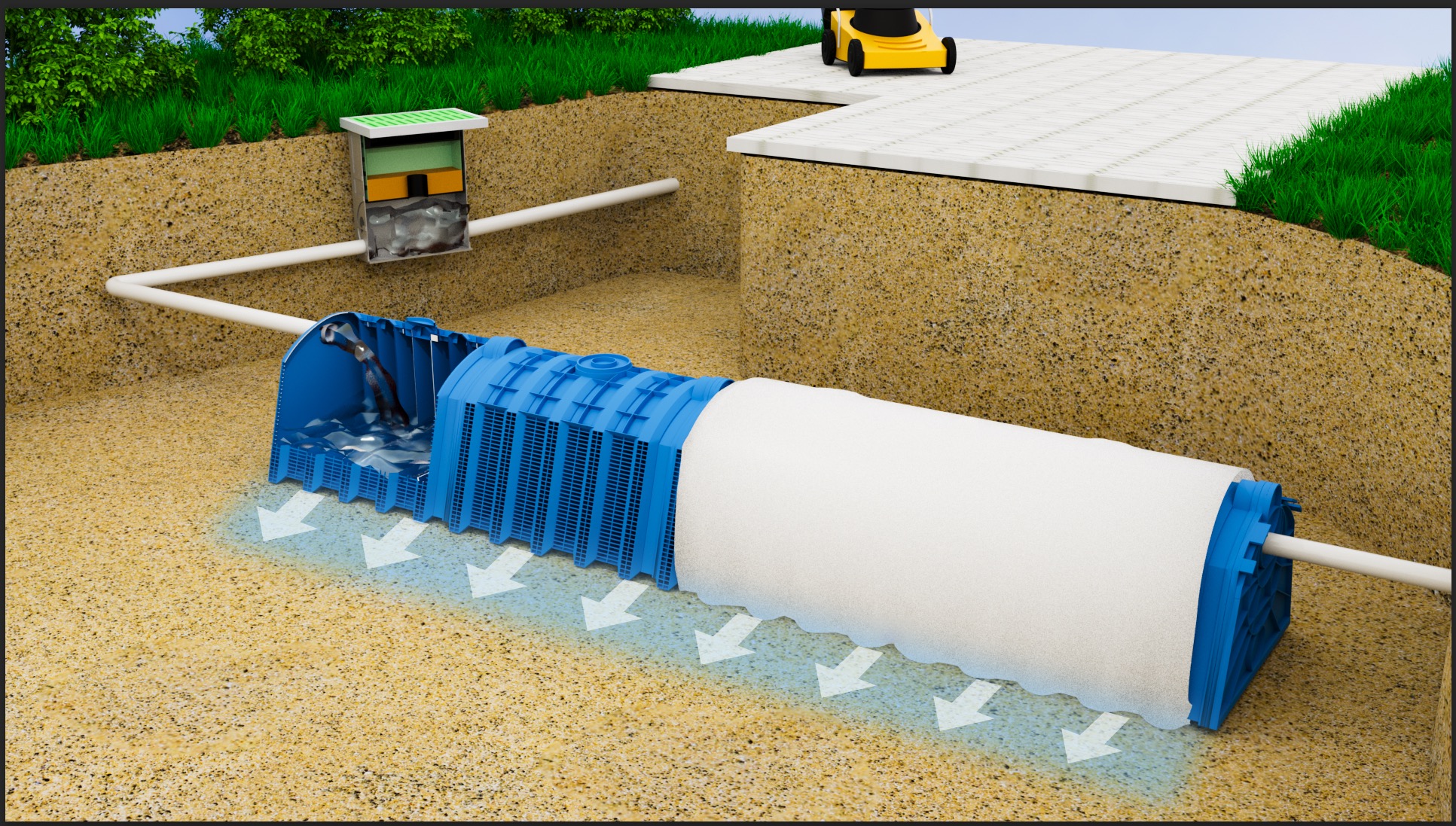
Rainwater attenuation is a process that involves capturing, storing, and slowly releasing rainwater to manage stormwater runoff and reduce flooding risks. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how rainwater attenuation works:
Step 1: Rainwater Collection
The first step in rainwater attenuation is collecting rainwater from various surfaces, primarily rooftops. This is typically done using gutters and downspouts that channel rainwater away from buildings and into the attenuation system.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Installed along the edges of roofs to collect and direct rainwater.
- Collection Points: Designated areas where rainwater is funneled into the attenuation system.
Step 2: Pre-filtration
Before the rainwater enters the storage system, it often goes through a pre-filtration process to remove debris, leaves, and other contaminants.
- Leaf Guards and Screens: Prevent large debris from entering the system.
- Sediment Filters: Capture smaller particles and sediments to ensure cleaner water storage.
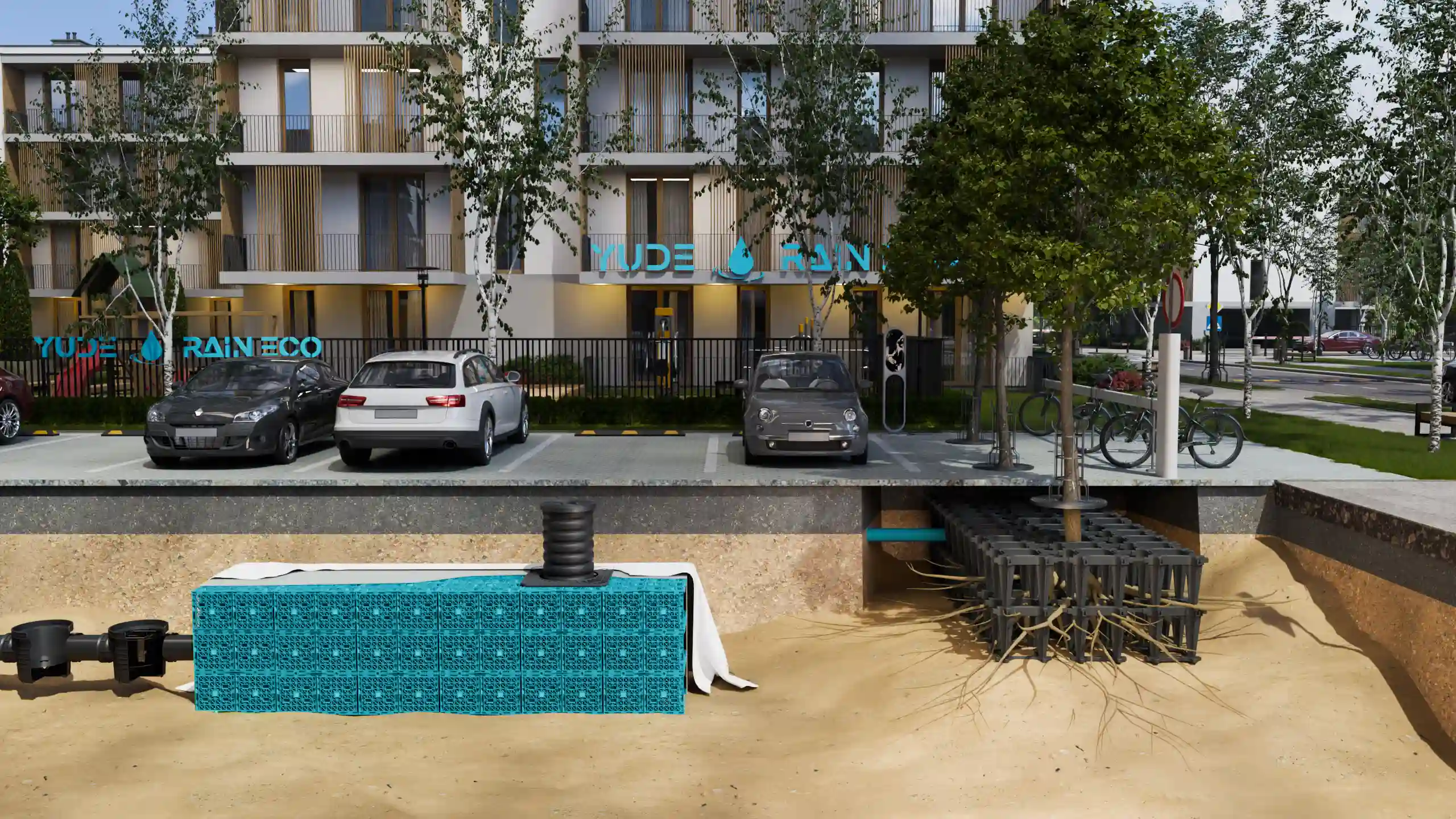
Step 3: Storage
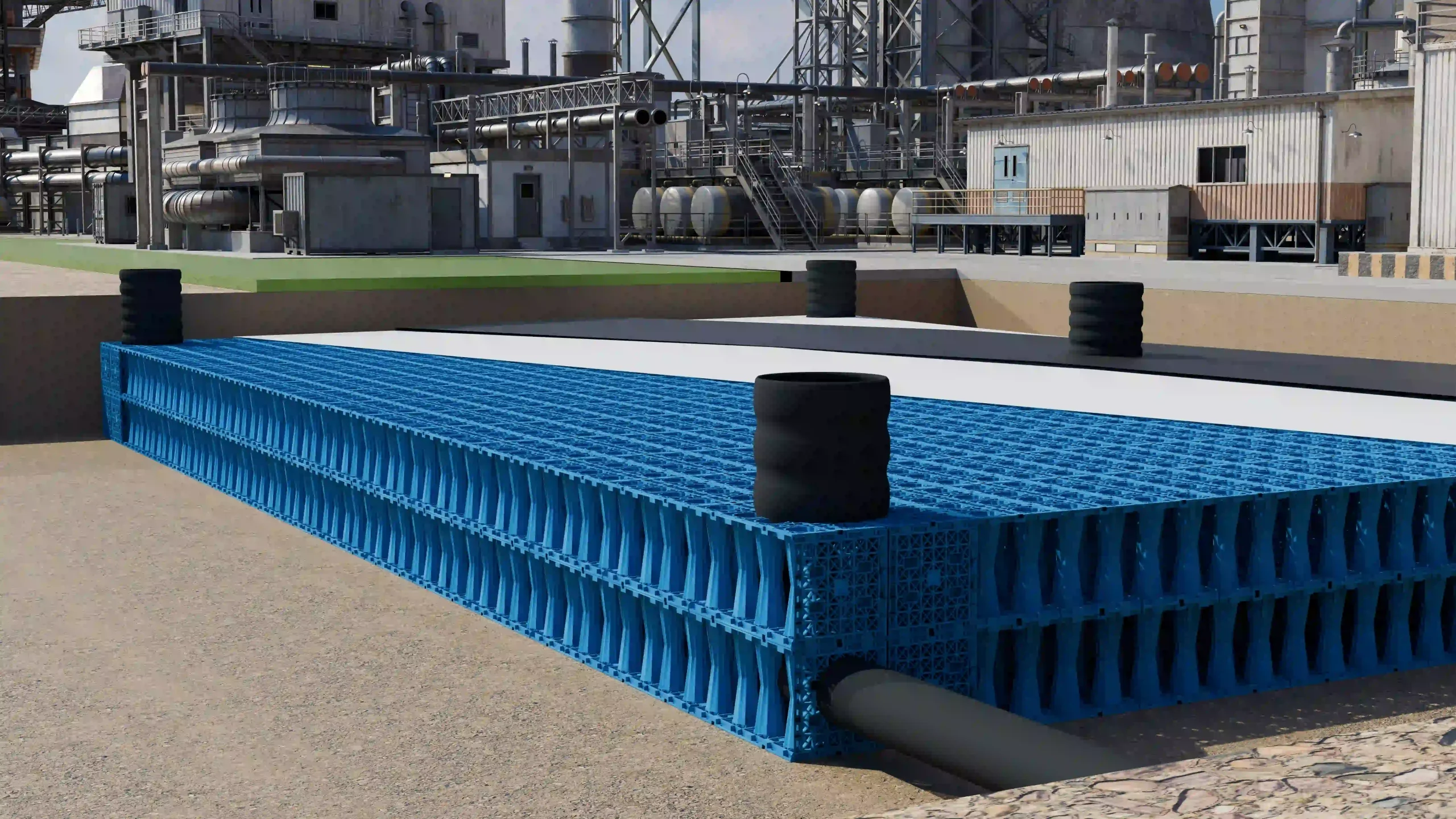
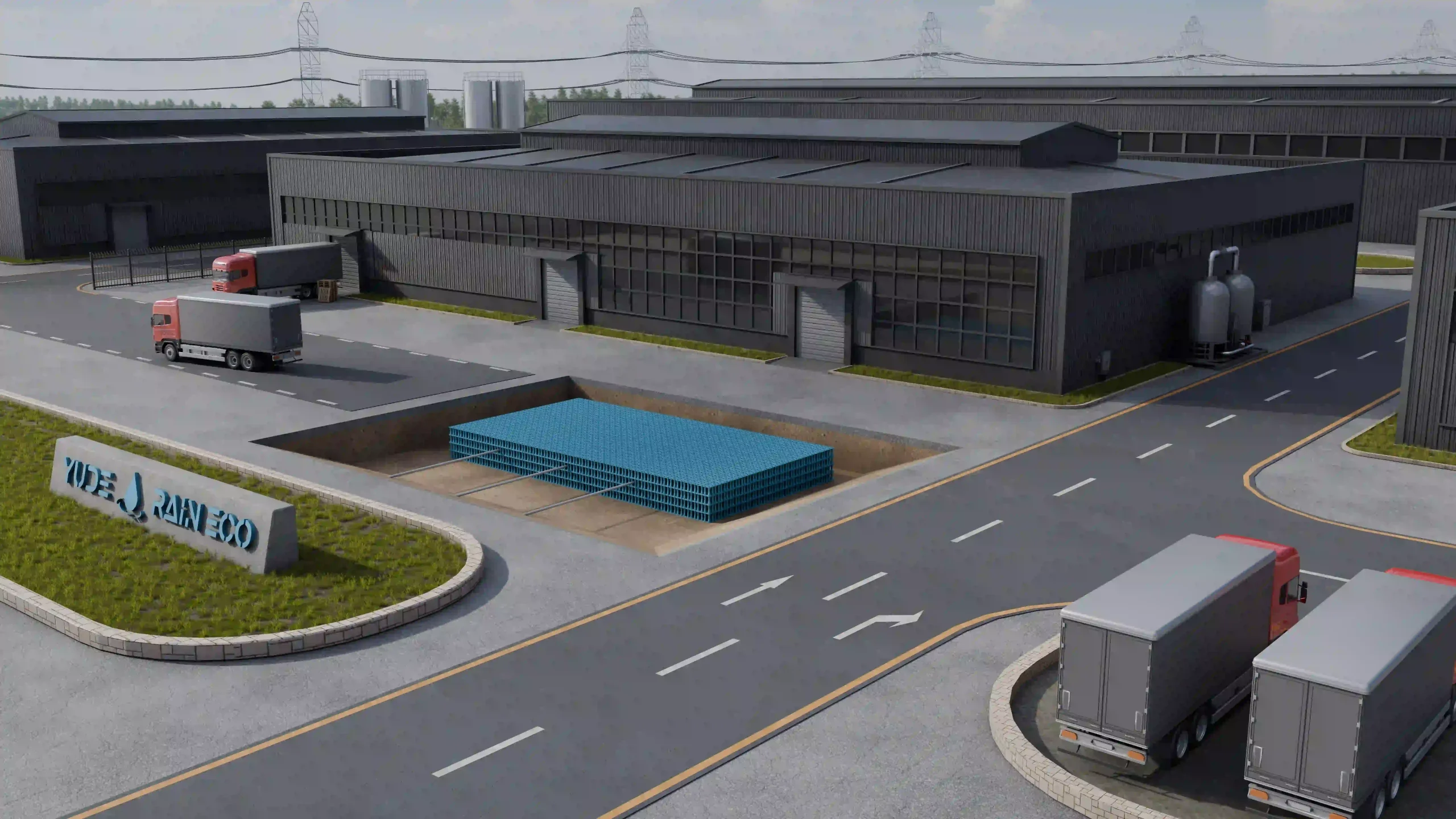
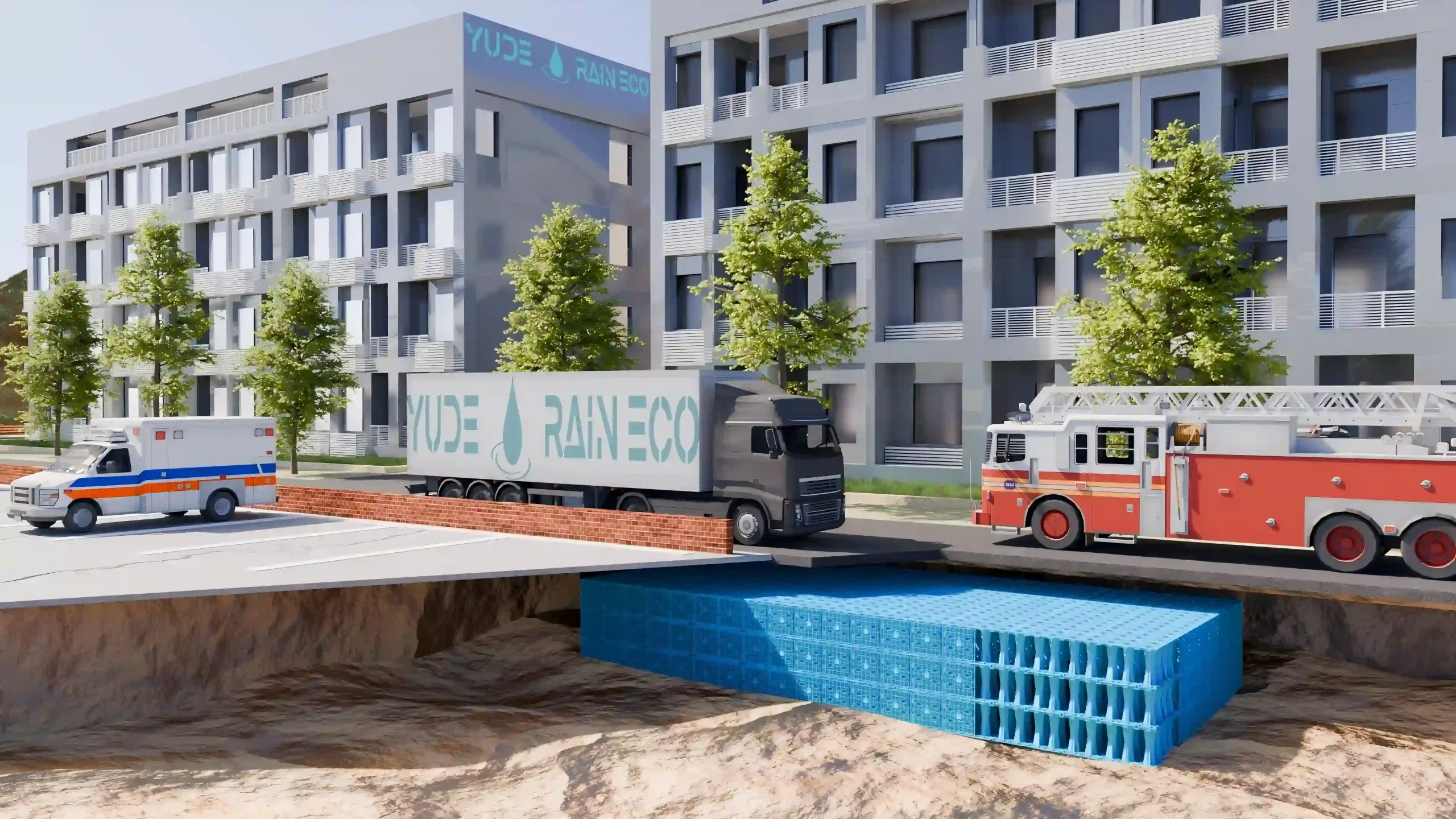
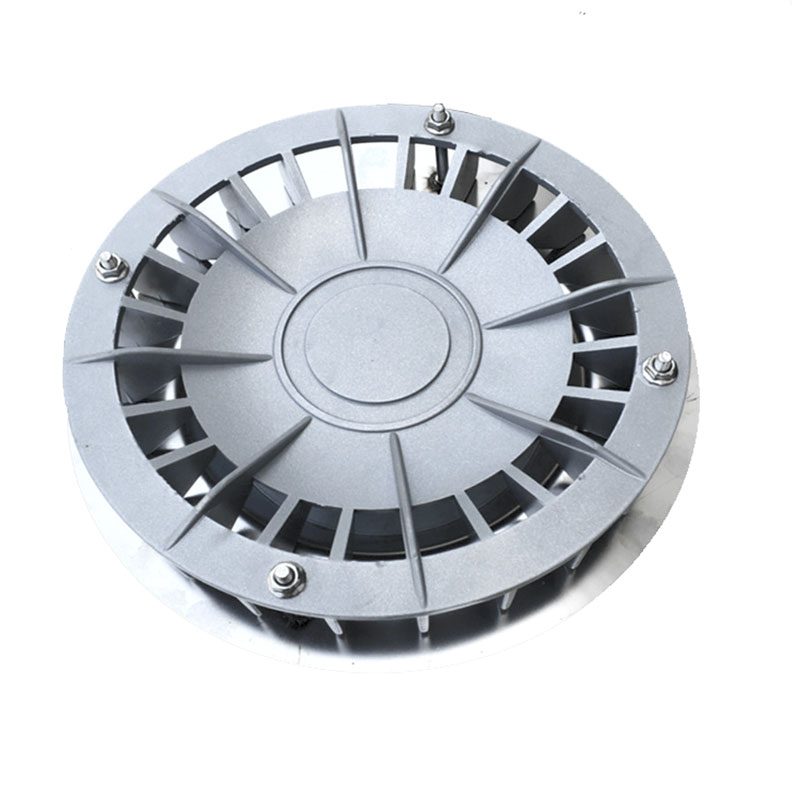
The filtered rainwater is then directed into storage tanks or attenuation cells. Crates used in attenuation systems are typically made of high-strength recycled polypropylene, offering both structural integrity and environmental benefits. These modular cells interlock to form underground reservoirs capable of withstanding heavy loads and long-term use.These storage units can be above ground, underground, or a combination of both, depending on the system design and available space.
- Underground Tanks: Typically made of materials like polypropylene, these tanks can store large volumes of water and are hidden from view.
- Attenuation Cells: Modular units that can be combined to create the desired storage capacity. They are flexible and can be configured to fit various site requirements.
Step 4: Controlled Release
One of the key components of rainwater attenuation is the controlled release of stored water. This process ensures that the drainage system is not overwhelmed during heavy rainfall events.
- Flow Control Devices: These devices regulate the rate at which water is released from the storage units into the drainage system.
- Orifice Plates and Valves: Commonly used to manage the flow rate, ensuring a steady and controlled discharge.
Some systems also integrate smart flow regulators or IoT sensors, which monitor water levels and control discharge in real-time, optimizing performance during varying rainfall intensities.
Step 5: Infiltration and Drainage
The controlled release water is then gradually discharged into the ground or the drainage system, reducing the immediate impact on local waterways and preventing flooding.
- Soakaways and Infiltration Trenches: Allow water to percolate into the ground, replenishing groundwater supplies.
- Drainage Channels: Direct water into the municipal drainage system or natural water bodies at a manageable rate.
Step 6: Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to ensure the rainwater attenuation system functions effectively. This includes inspecting and cleaning gutters, filters, and storage units.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check for blockages, leaks, and system integrity.
- Cleaning and Servicing: Keep the system free from debris and ensure all components are working correctly.
Types of Rainwater Attenuation Systems
There are several types of rainwater attenuation systems, including:
- Underground Attenuation Tanks: These large, buried tanks store significant volumes of rainwater.
- Attenuation Cells: Modular units that can be customized to fit specific needs.
- Green Roofs: Vegetated roofs that absorb rainwater and reduce runoff.
- Permeable Pavements: Surfaces that allow rainwater to infiltrate the ground, reducing surface runoff.
- Smart Attenuation Systems: These utilize digital monitoring tools to manage stormwater retention and discharge dynamically, ideal for smart city infrastructure.
Factors to Consider When Implementing Rainwater Attenuation Crates
- Site Characteristics: Soil type, groundwater levels, and topography influence system design.
- Storage Capacity: Determine the required volume based on local rainfall data.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance ensures system efficiency and longevity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local regulations and guidelines is crucial.
Additional assessments such as percolation rate testing and infiltration modeling are essential to ensure effective system performance. These factors determine whether a crate-based attenuation system should integrate with soakaways or rely entirely on outflow control.
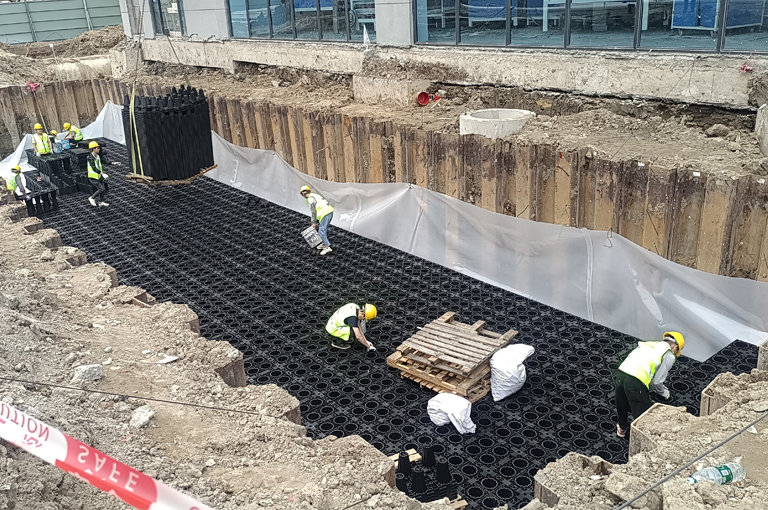
Rainwater Attenuation Tank Installation
Rainwater Attenuation Tank Installation
Proper installation of attenuation crates involves several key steps:
-
Excavation: A pit is excavated based on the calculated storage volume, ensuring a flat and compacted base.
-
Geotextile and Lining: A permeable or impermeable geotextile membrane is laid depending on whether infiltration is desired.
-
Crate Assembly: The crates are assembled and stacked as per the design, ensuring structural stability.
-
Connection to Inlets and Outlets: Pipes are connected to control inflow and outflow, and inspection points are installed for maintenance.
-
Backfilling and Restoration: The area is backfilled and can be landscaped, paved, or built over, depending on design requirements.

Case Studies of Successful Rainwater Attenuation Projects
Numerous successful projects globally highlight the effectiveness of rainwater attenuation. For example, urban areas in the Netherlands and Germany have implemented large-scale attenuation systems, significantly reducing flooding and improving water quality.
Learn our Case Study. These case studies underscore the transformative potential of rainwater attenuation in urban water management.
Government Regulations and Incentives for Rainwater Attenuation Crates
Governments around the world are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable water management and are implementing regulations and incentives to promote rainwater attenuation. However, the approach varies significantly by country.
Countries Supporting Rainwater Attenuation Crates
Germany: Germany is a leader in rainwater management, with extensive regulations promoting the use of rainwater harvesting and attenuation. Cities like Berlin and Hamburg offer financial incentives and grants to encourage the implementation of these systems.
Netherlands: Known for its advanced water management systems, the Netherlands provides subsidies and tax incentives for rainwater attenuation projects. The government also mandates the incorporation of sustainable water management practices in new developments.
Australia: Australian states like New South Wales and Victoria offer rebates and grants for installing rainwater tanks and attenuation systems. The country’s focus on water conservation has led to widespread adoption of these practices.
United Kingdom: The UK government supports sustainable drainage systems (SuDS), including rainwater attenuation, through regulatory frameworks and financial incentives. Local authorities often provide grants to support the installation of these systems in urban areas.
Countries with Restrictions or Bans
United States (Certain States): While rainwater harvesting and attenuation are encouraged in many US states, some states have restrictions or bans. For example, in Colorado, historical water rights laws restrict the collection of rainwater without a permit, although recent legislation has eased some of these restrictions.
Parts of the Middle East: In some Middle Eastern countries, the scarcity of rainfall and the need to preserve traditional water rights have led to restrictions on rainwater harvesting. However, these restrictions are gradually being reconsidered in light of growing water scarcity issues.
Incentives and Regulations
- Grants and Subsidies: Many governments offer financial support to encourage the adoption of rainwater attenuation systems. These can include direct grants, subsidies for installation costs, and tax rebates.
- Regulatory Requirements: Some regions have made the incorporation of rainwater attenuation systems mandatory in new construction projects. This includes specific design criteria to ensure systems are effective and sustainable.
- Educational Programs: Governments also promote awareness and education about the benefits of rainwater attenuation, helping to drive community adoption and support.
Staying informed about local regulations and available incentives is crucial for property owners and developers looking to implement rainwater attenuation systems. By leveraging these supports, they can contribute to sustainable water management and enhance their projects’ environmental impact.
Cost-Effectiveness of Rainwater Attenuation Crates
Investing in rainwater attenuation systems can be highly cost-effective. These systems reduce the need for expensive stormwater infrastructure and prevent flood damage, leading to substantial savings. Additionally, reusing stored rainwater can lower water bills, contributing to overall cost efficiency. Long-term financial modeling shows that attenuation systems can reduce lifecycle costs for urban drainage by up to 30% compared to conventional piped systems. Their modularity also allows for phased installation, spreading out capital investment.
Integration with Broader Stormwater Management Strategies
Rainwater attenuation crates are most effective when integrated into a comprehensive stormwater management plan. They can be combined with bioswales, infiltration basins, rain gardens, and permeable paving to form a holistic sustainable urban drainage system (SuDS). This integration enhances biodiversity, improves urban microclimates, and supports climate adaptation.
Embracing Rainwater Attenuation for a Sustainable Future
Rainwater attenuation is crucial for sustainable urban water management. By understanding its benefits, implementation methods, and regulatory landscape, communities can effectively incorporate these systems to enhance resilience, conserve water, and minimize environmental impact. Embracing rainwater attenuation is a vital step towards a sustainable future, ensuring water security and environmental protection for generations to come.
Call to Action
Yude Rain Eco specialize in providing advanced rainwater attenuation solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of urban environments. Our innovative systems are designed to manage stormwater effectively, reduce flood risks, and promote sustainable water use. Contact us today to learn more about how our rainwater attenuation solutions can benefit your project and contribute to a sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a rainwater attenuation tank and a soakaway?
A soakaway allows water to infiltrate into the ground, primarily for areas with permeable soil. A rainwater attenuation tank, especially with impermeable lining, stores and slowly releases stormwater to prevent flooding, regardless of soil permeability.
Can attenuation crates be installed under driveways or buildings?
Yes. Heavy-duty rainwater attenuation crates are designed to support high traffic loads, including vehicles and light structural loads. Ensure the system design follows load class guidelines.
Do rainwater attenuation tanks require maintenance?
Yes. Regular inspection and maintenance of filters, inspection chambers, and flow control devices are essential to ensure optimal performance and system longevity.
How long do attenuation crates last?
High-quality crates, like those made from reinforced polypropylene, typically have a design life of 50 years or more when installed and maintained properly.
Are rainwater attenuation systems mandatory for new developments?
In many jurisdictions (e.g., UK, Germany, Australia), local planning authorities require sustainable drainage solutions, including attenuation systems, for new developments to comply with environmental regulations.















