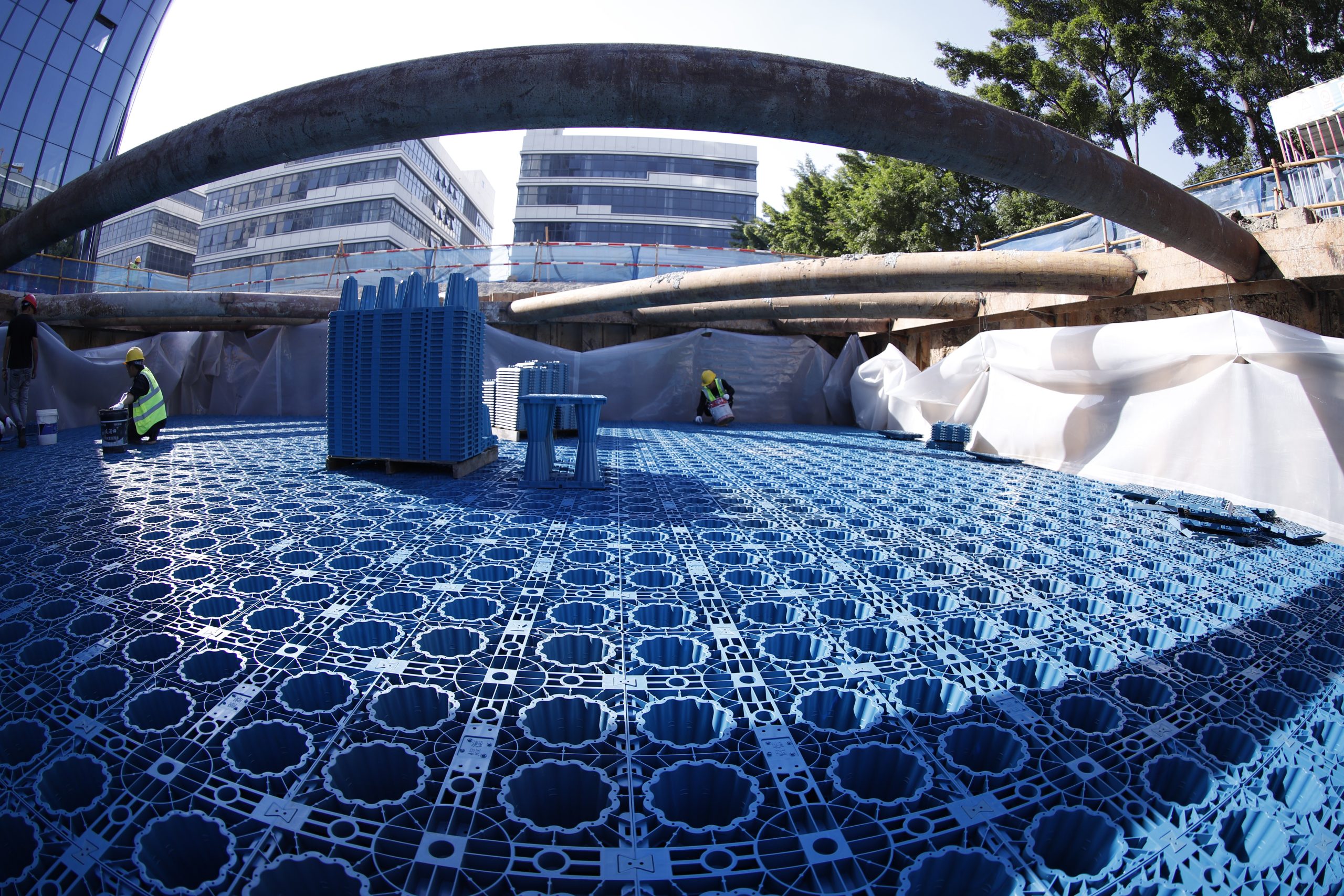
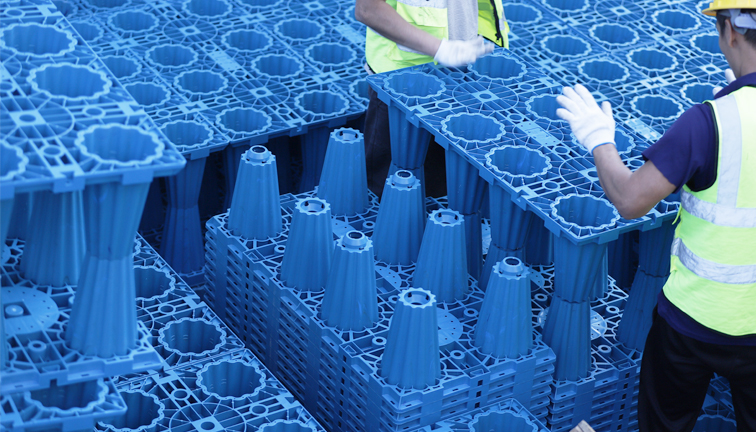
As urban development continues to grow and environmental challenges like water scarcity and climate change become more pressing, the question of whether to install underground rainwater harvesting systems in buildings has gained importance. Rainwater harvesting offers significant advantages for both the environment and property owners, but is it worth the investment? In this article, we will explore the reasons for installing these systems, the risks of not installing them, and the potential long-term benefits, especially when paired with modern siphon drainage systems. We will also cover the installation process, the lifespan of these systems, and maintenance guidelines. This comprehensive analysis will help building owners, developers, and architects make informed decisions.
1. Why Install Rainwater Harvesting and Siphon Drainage Systems in Buildings?
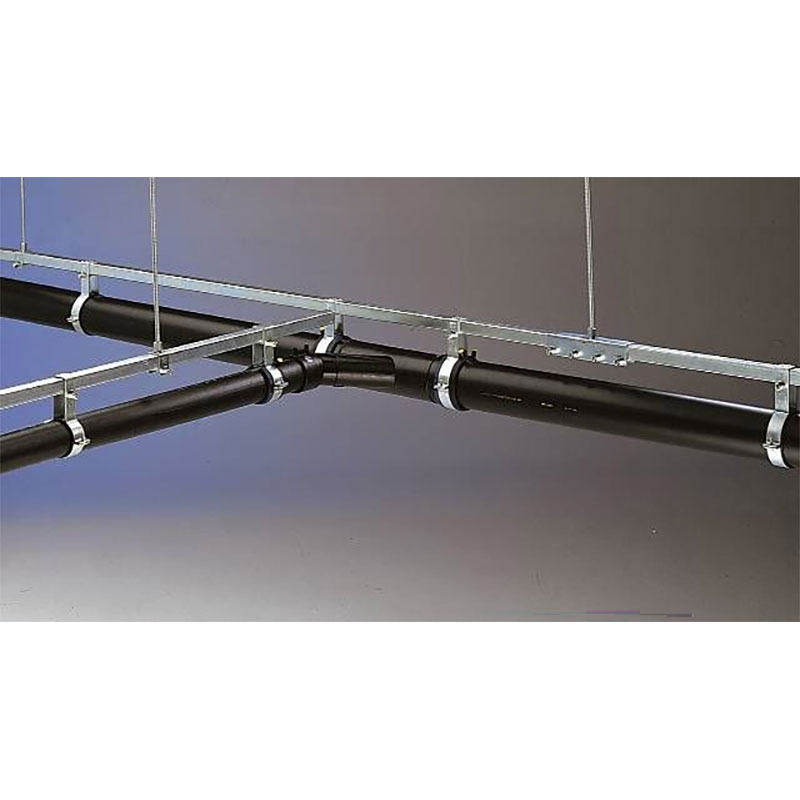
Rainwater harvesting systems, especially underground ones, have become essential components of sustainable building design. When combined with siphon drainage systems, they create an efficient water management solution that benefits both the environment and the building owner.
Hazards of Excessive or Prolonged Rainfall on Buildings
Excessive rainfall poses several risks to buildings, particularly in urban areas where impermeable surfaces like roads and roofs limit natural water absorption. The risks include:
- Flooding: Prolonged heavy rainfall can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to localized flooding that damages building foundations, basements, and even ground-level structures. According to a report by the U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), water damage from flooding is one of the most costly repairs for buildings, often requiring substantial remediation.
- Foundation Erosion: Excessive rainwater that is not managed properly can seep into the soil around the building, causing the soil to erode or swell, destabilizing the foundation. The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) warns that poor water management can lead to serious structural damage over time.
- Waterproofing Failure: Buildings designed without adequate rainwater drainage can experience water infiltration through walls, roofs, and windows. Over time, this can degrade waterproofing materials, leading to leaks and water damage within the building’s interior.
- Mold and Mildew Growth: Excess moisture due to inefficient rainwater management can lead to mold and mildew growth inside buildings. This is not only a structural problem but also a significant health hazard.
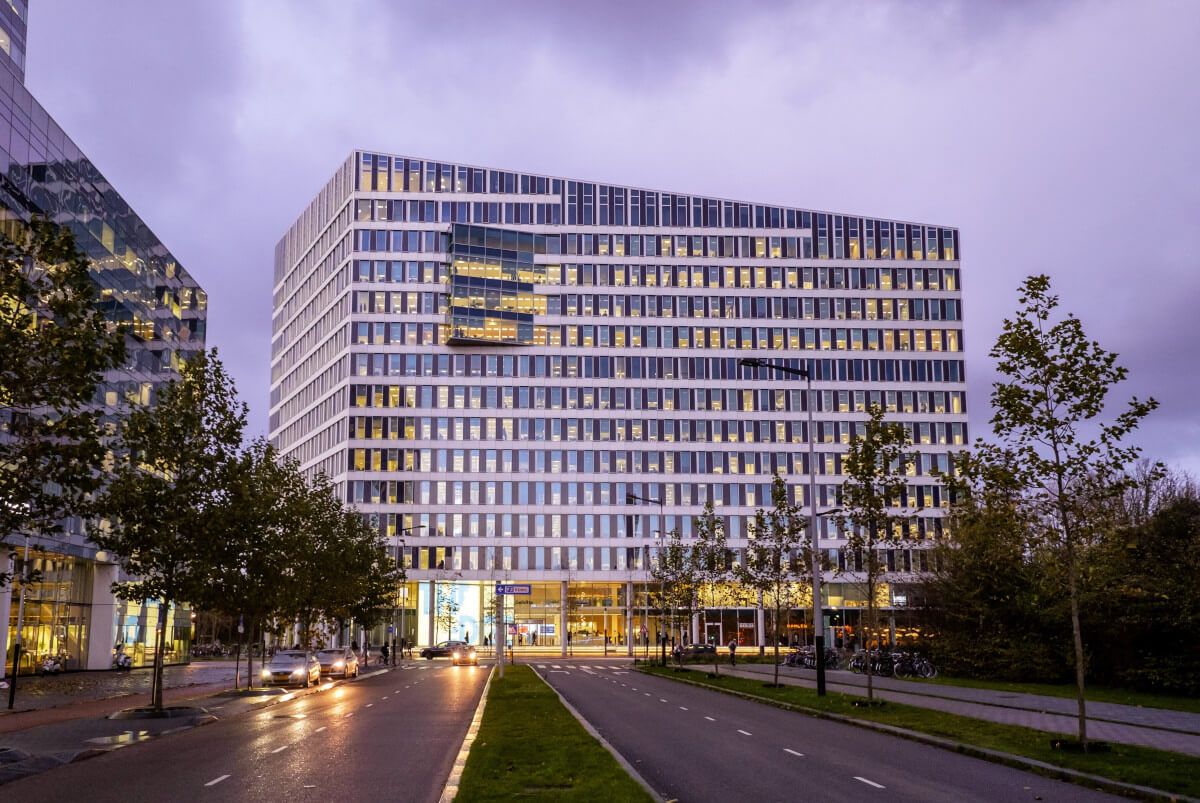
Case Study 1: The Edge, Amsterdam
The Edge, often considered one of the most sustainable office buildings in the world, incorporates an advanced underground rainwater harvesting system. This system has a capacity of 50,000 liters and collects rainwater from the building’s roof. The collected rainwater is used for toilet flushing and irrigation, significantly reducing the building’s reliance on municipal water supplies. The Edge is a model for how modern buildings can integrate rainwater harvesting to address challenges like flooding and water conservation while maintaining structural integrity.

2. Benefits of Underground Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Buildings
Underground rainwater harvesting systems provide a multitude of benefits to both residential and commercial buildings. From environmental sustainability to financial savings, these systems offer an array of advantages that make them a smart investment.
Flood Prevention
One of the primary benefits of installing an underground rainwater harvesting system is flood prevention. By capturing and storing rainwater that would otherwise contribute to stormwater runoff, these systems reduce the risk of flooding in urban areas. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), stormwater runoff is a major cause of urban flooding, and managing this runoff through harvesting systems is one of the most effective solutions.
Siphon drainage systems further enhance flood prevention by creating an efficient and rapid drainage process. Unlike conventional drainage systems, which rely on gravity and can become overwhelmed by heavy rainfall, siphon systems use negative pressure to move large volumes of water quickly and efficiently, reducing the risk of overflows and backups.
Water Cost Savings
Rainwater harvesting also contributes to significant cost savings by providing a free, renewable source of water for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and even cooling systems. According to the World Bank, water scarcity will drive up water costs globally in the coming decades, making water-efficient systems like rainwater harvesting critical for reducing operational expenses. Buildings that install these systems can save 30-50% on their water bills, depending on the building’s water needs and the local climate.
Case Study 2: 22 Bishopsgate, London
22 Bishopsgate, one of London’s most iconic skyscrapers, features a 1,500 cubic meter underground rainwater harvesting system. The system is designed to capture and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as HVAC cooling and toilet flushing. The building’s innovative water management system helps reduce its overall water demand by nearly 40%, making it a key example of how high-rise buildings can integrate sustainable water solutions to enhance both operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.

Building Protection and Longevity
Water is a building’s worst enemy when it comes to structural integrity. Proper management of rainwater through underground storage tanks and siphon drainage systems helps protect buildings from water damage, preserving their structural integrity over the long term. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) notes that water infiltration and poor drainage are responsible for many building failures, and rainwater management systems can extend the lifespan of a structure by reducing wear and tear.
3. What Are the Differences Between Installing and Not Installing Rainwater Harvesting and Siphon Drainage Systems?
Buildings That Install These Systems:
- Flood Prevention: With underground rainwater storage and siphon drainage, these buildings are better protected from flooding and stormwater issues.
- Cost Savings: Significant savings in water costs, particularly in regions where water is expensive or scarce.
- Long-Term Durability: Better protection of the building’s foundation and structure, leading to fewer maintenance issues and longer building lifespan.
- Environmental Impact: Buildings that install rainwater harvesting systems contribute to water conservation efforts and reduce their environmental footprint.
Buildings That Do Not Install These Systems:
- Flood Risk: Higher susceptibility to water damage during storms and heavy rainfall.
- Increased Water Costs: Complete reliance on municipal water supplies for all uses, resulting in higher water bills.
- Structural Degradation: Potential for foundation erosion, water infiltration, and mold growth, leading to more frequent repairs and maintenance costs.
- Higher Environmental Impact: Increased pressure on local water sources and higher consumption of treated potable water for non-potable purposes.
Case Study 3: Gardens by the Bay, Singapore
Gardens by the Bay is a landmark project in Singapore known for its sustainability initiatives. The underground rainwater harvesting system in the facility has a capacity of 2 million liters, collecting rainwater for irrigation of the park’s extensive gardens and landscaping. The system also prevents flooding by managing excess stormwater, a critical feature in a city known for its heavy rainfall. Gardens by the Bay showcases the scalability of underground rainwater harvesting systems and their ability to serve large, public spaces while contributing to environmental conservation.

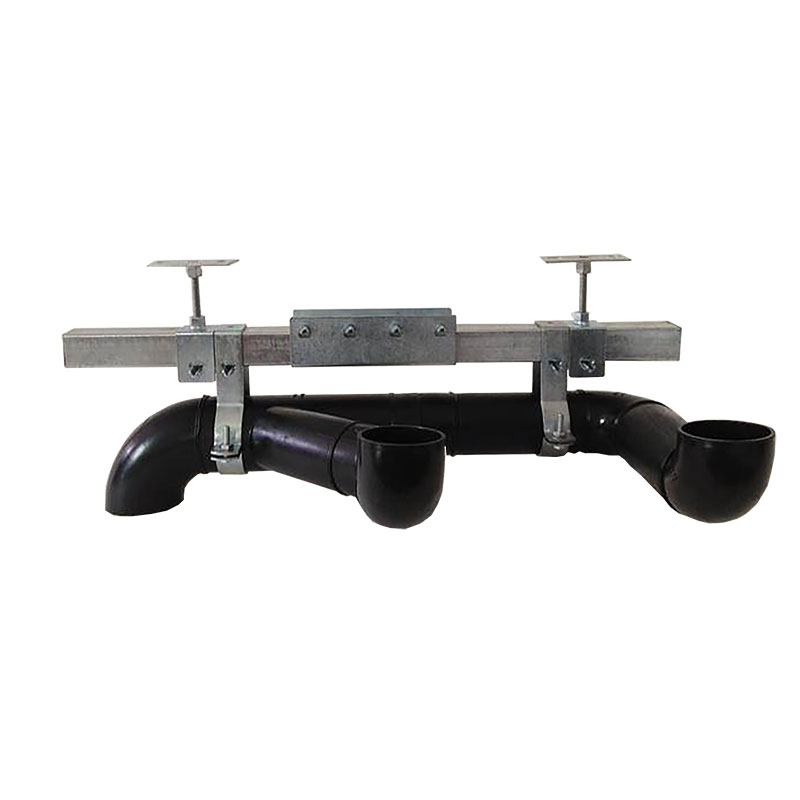
4. How to Install a Proper Underground Rainwater Harvesting System
A proper rainwater harvesting system requires careful planning, from design to installation, to ensure it meets the building’s water management needs and local regulations.
- Site Analysis: The first step is a thorough analysis of the site, including the roof area, local rainfall data, and the building’s water usage requirements. Yude Rain Eco will assist you in calculating your building’s average water demand for irrigation, toilet flushing, and other non-potable water uses to determine and recommend the appropriate storage tank size.
- System Design: The design must integrate the rainwater collection system with the building’s existing plumbing and landscape irrigation systems. Additionally, the system should include filtration and treatment options to ensure water quality for the intended uses.
- Regulatory Compliance: It’s crucial to check local regulations regarding rainwater harvesting. In some areas, permits may be required for installing large storage tanks or siphon drainage systems.
5. How Long Does an Underground Rainwater Harvesting System Last?
The lifespan of an underground rainwater harvesting system depends on the materials used, the quality of installation, and ongoing maintenance. High-quality polypropylene or concrete storage tanks can last for over 50 years with minimal maintenance, according to the International Rainwater Harvesting Alliance (IRHA). Pumps and filtration systems typically have shorter lifespans, ranging from 10-20 years, and may need to be replaced or upgraded over time.
Are the Benefits Worth the Extra Construction Costs?
The initial investment in an underground rainwater harvesting system can be significant, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs. A study by the Global Water Research Coalition (GWRC) found that the payback period for rainwater harvesting systems in commercial buildings is typically between 5 and 10 years, depending on the size of the system and local water costs. The combination of flood prevention, water savings, and building protection makes it a worthwhile investment for many property owners.
6. Maintenance Q&A
- Q1: How often should the underground rainwater harvesting system be inspected?
- A: It’s recommended to conduct inspections annually, although buildings in areas with frequent heavy rainfall may require more frequent checks. During inspections, focus on checking for leaks, sediment buildup in the tank, and proper functioning of pumps and filters. Also, inspect the siphon drainage system after major storms to ensure there are no blockages or damage.
- Q2: How often should the filters be replaced or cleaned?
- A: Filters in the system should be cleaned or replaced every 6 to 12 months, depending on the water quality and usage. Pre-filtration systems like gutter guards and first-flush diverters should be cleaned more frequently to prevent debris from entering the storage tank.
- Q3: What maintenance do the pumps require?
- A: Pumps should be inspected regularly for any signs of wear, leaks, or reduced performance. Ensure that all moving parts are functioning properly, and replace any worn or damaged components. The pump’s life expectancy varies but generally lasts around 10-20 years, depending on use and maintenance.
- Q4: What should be done if sediment builds up in the storage tank?
- A: Over time, sediment may accumulate at the bottom of the tank. To maintain water quality and system efficiency, it’s important to remove this sediment periodically. Sediment removal should be done every few years, depending on the amount of debris that enters the system.
- Q5: How can I ensure the siphon drainage system continues to function properly?
- A: The siphon drainage system should be monitored, especially after heavy rain, to ensure it is free from blockages. Regularly check for debris in the drainage pipes and inspect the siphon mechanisms to ensure they are creating the proper negative pressure needed for efficient drainage.

- Q6: Do underground tanks require any specific protection against freezing?
- A: Underground tanks are typically installed below the frost line, which protects them from freezing. However, in extremely cold climates, additional insulation or frost protection measures may be needed for the pipes and pumps. Always consult with a professional to determine the best protection methods for your specific region.
Are You Ready to Invest in Sustainable Water Management for Your Building?
Yude Rain Eco specialize in designing and installing advanced underground rainwater harvesting and siphon drainage systems that meet your building’s unique water management needs. Whether you’re looking to prevent flooding, save on water costs, or reduce your environmental footprint, we have the expertise to help you achieve your goals.
Contact us today for a free consultation and learn how our systems can protect your building while promoting sustainability.