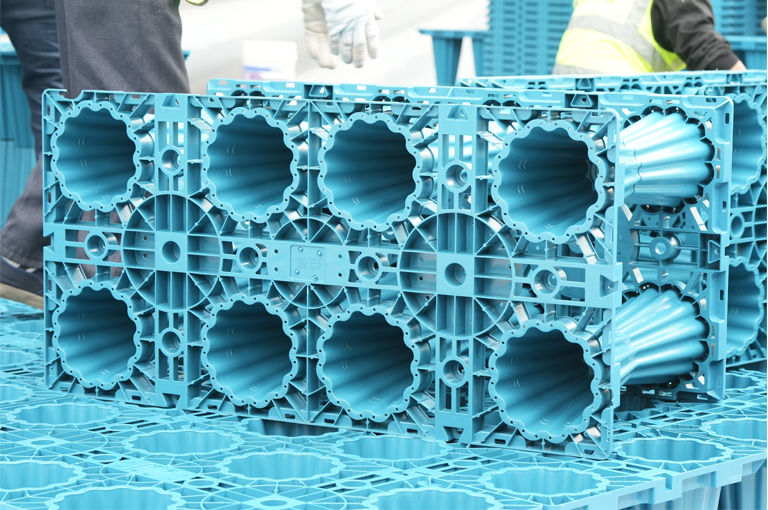
Rainwater (runoff from rain, snowmelt, or ice melt) might seem harmless, but if left uncontrolled, it can lead to costly flooding and pollution issues, significantly harming our communities. Implementing sustainable stormwater management within building facilities, also known as Low Impact Development (LID) or green infrastructure, is crucial. Sustainable stormwater management aims to reduce runoff and enhance water quality. LID practices help maintain the natural hydrological cycle through site grading, vegetation, soil, and natural processes that absorb and filter rainwater on-site. These practices also help minimize erosion, flooding, and water pollution downstream from the building facilities.
Since we cannot control the weather, implementing Best Management Practices (BMPs) for stormwater through Yude is one of the most effective ways to avoid the consequences of excessive runoff. BMPs can help you:
- Reduce stormwater runoff from your property and its associated impacts, including erosion, basement flooding, and sewer blockages.
- Meet National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit requirements.
- Supplement your Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP).
Here are some BMPs and LID practices Yude employs to reduce stormwater runoff and pollution:
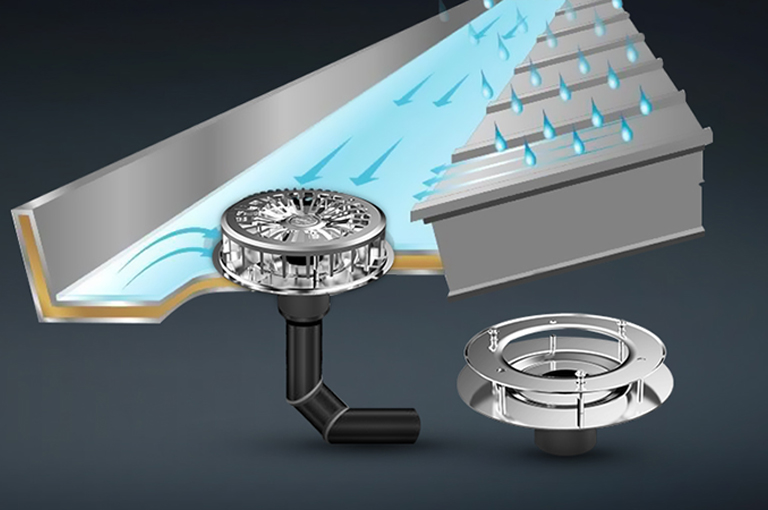

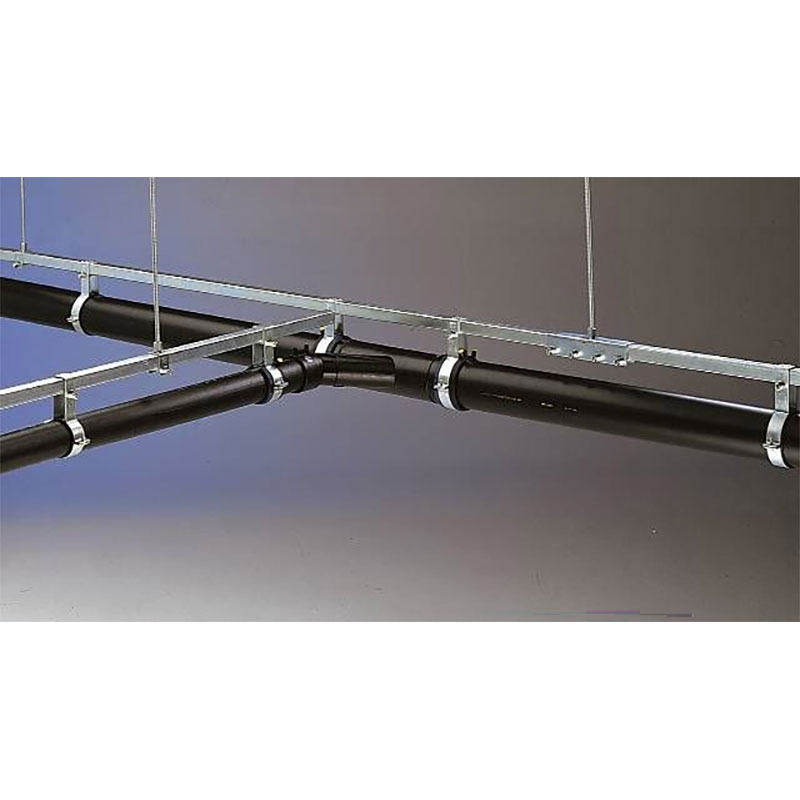
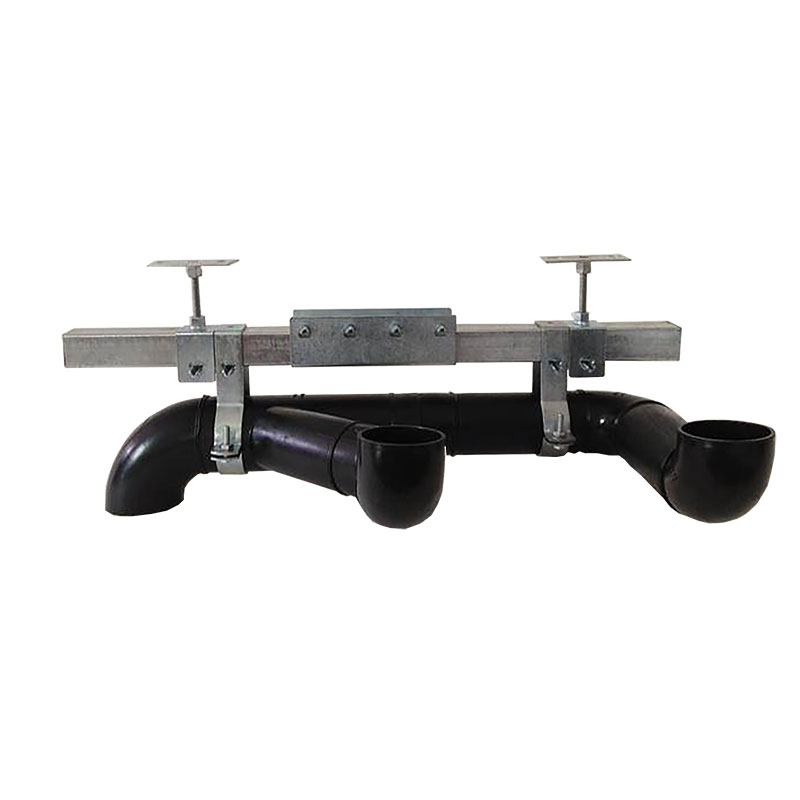
1. Siphonic Roofs
A siphonic roof is a design that uses the siphon principle for rainwater drainage. It effectively drains rainwater from the roof through a special siphonic drainage system, preventing water accumulation and potential structural damage. The siphonic roof is covered by a full set of siphonic drainage systems, allowing rainwater to be discharged timely and efficiently.
It can:
- Quickly drain water: Efficiently discharging rainwater from the roof, preventing accumulation.
- Reduce roof load: Lower the burden on the roof caused by water accumulation, extending the building’s lifespan.
- Protect the building structure: Prevent leaks and structural damage caused by water pressure.
Applications Siphonic roofs are widely used in:
- Large public buildings: such as stadiums, airports, and shopping centers, where roof areas are large, and rainwater drainage demands are high.
- Industrial plants: which require efficient drainage systems to prevent damage to production equipment.
- Commercial buildings: such as office buildings and hotels, requiring quick drainage to maintain the building’s safety and aesthetics.
Advantages
- Efficient drainage: The siphonic effect speeds up rainwater discharge, suitable for large roof areas.
- Flexible pipe arrangement: Siphonic systems are not affected by terrain, allowing flexible design and installation of pipes.
- Reduced construction cost: Compared to traditional gravity drainage systems, siphonic systems require smaller pipe diameters, saving materials and space.
Disadvantages
- High initial cost: The design and installation of siphonic systems are more demanding, requiring significant initial investment.
- Complex maintenance: The system requires the pipes to remain sealed, necessitating regular inspections and maintenance costs.
- High installation requirements: Ensuring system precision and sealing during construction requires professional skills and equipment.
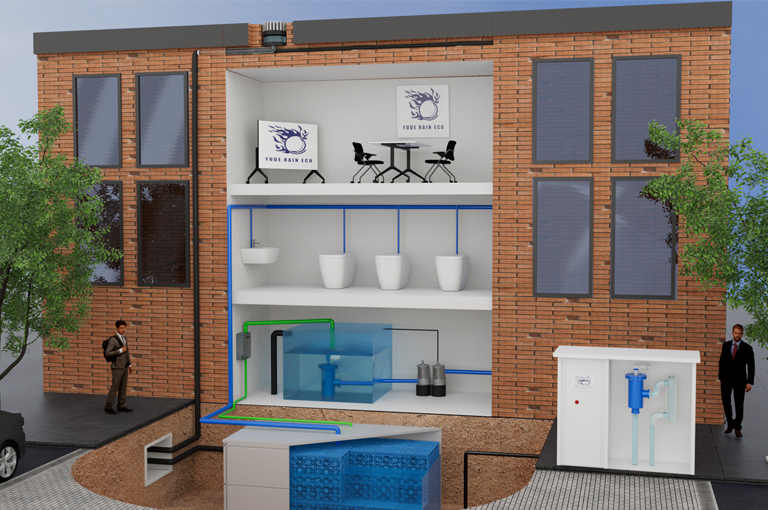

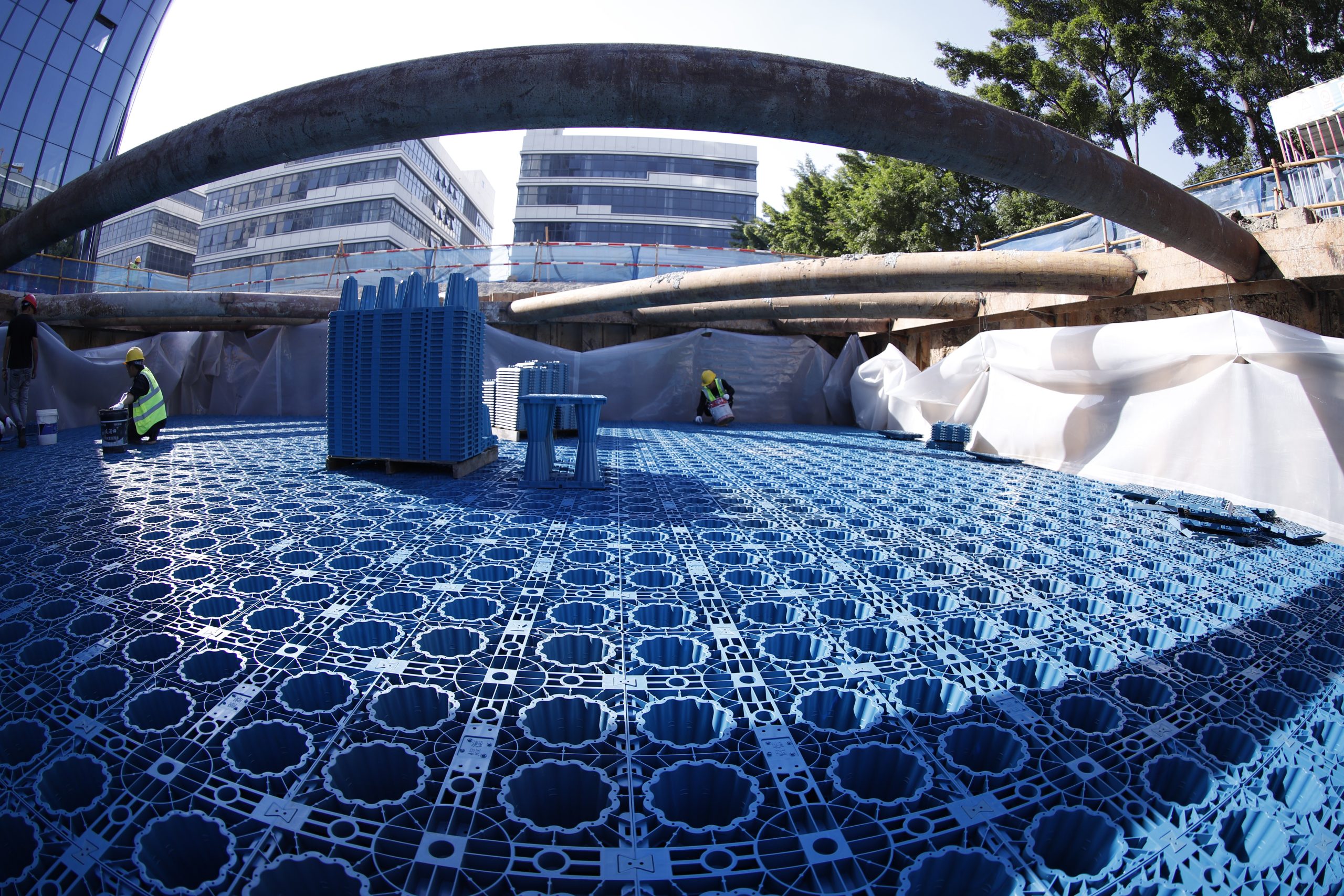
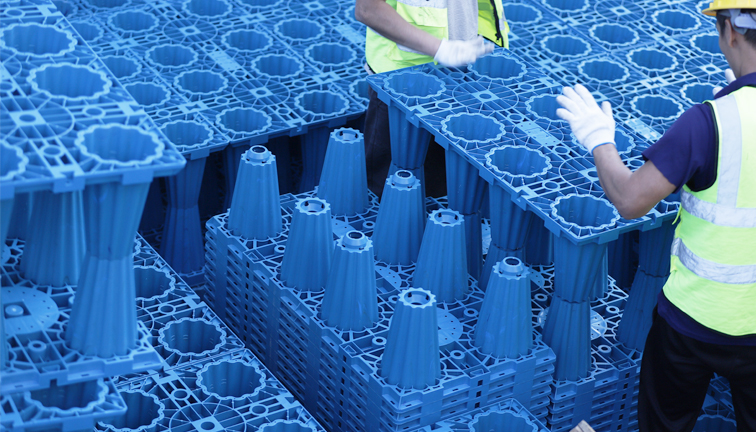
2. Underground Rainwater Cisterns
Underground rainwater cisterns are man-made lakes or underground reservoirs designed to handle stormwater runoff by mimicking the water treatment capabilities of natural watersheds. Runoff collected in the basin undergoes natural treatment processes:
- Sedimentationhelps remove particles, organic matter, and metals.
- Biological absorptionby plants, algae, and bacteria can further remove pollutants.
Underground rainwater cisterns maintain a constant water level and only release water to receiving waters during major storm events, differentiating them from dry ponds and other retention ponds.
Applications Underground rainwater cisterns are a good solution for any application with ample land. They can also replace existing detention ponds. Underground rainwater cisterns are best suited for areas with high soil permeability, allowing water to pass through quickly and lowering water levels.
Advantages Besides serving as stormwater control measures, these artificial ponds can:
- Significantly improve water quality.
- Recharge groundwater.
- Enhance community aesthetics.
- Have a lifespan of over 20 years if properly maintained.
- Combine with stormwater infiltration drains.
Disadvantages Like dry ponds, underground rainwater cisterns are not suitable for all locations. High initial costs and several critical considerations include:
- Identifying potential disruptions to surrounding wetlands and/or groundwater contamination during the initial design and construction phases is crucial. Any significant design flaws can lead to water quality deterioration.
- Regular inspections of surrounding vegetation and periodic evaluations of the structural integrity are necessary post-construction.
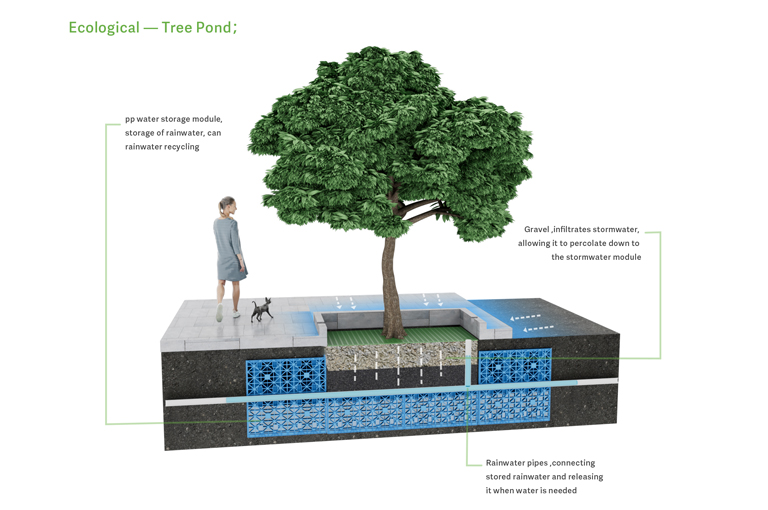
3. Eco Tree Ponds
Eco tree ponds are landscaped depressions that allow runoff to gather in designated areas and filter through soil and vegetation. Also known as urban forests, eco tree ponds integrate urban greening with stormwater management by planting trees and employing rainwater infiltration and filtration techniques to improve the urban environment and water resource efficiency.
It can:
- Beautify the city: Provide green landscapes, enhancing urban environmental quality.
- Manage stormwater: Reduce surface runoff, preventing urban flooding.
- Purify water: Filter pollutants from rainwater, improving water quality.
- Mitigate heat island effect: Bring ecological balance to the city, reducing the heat island effect.
Applications Eco tree ponds are widely used in:
- Urban roads: Set along sidewalks and roadsides for greening and stormwater management.
- Parks and plazas: Set in public green spaces and plazas to enhance landscaping and ecological functions.
- Commercial and residential areas: Set around buildings to improve the environment and stormwater management.
Advantages
- Eco-friendly and energy-saving: Utilizes natural filtration systems without requiring energy-consuming equipment.
- Environmental improvement: Increases urban green coverage, improving air quality and city appearance.
- Flood risk reduction: Effectively manages stormwater, lowering the risk of urban flooding.
- Maintains ecological balance: Provides diverse habitats, promoting urban biodiversity.
Disadvantages
- High initial investment: Construction costs are high, especially for large-scale applications.
- High maintenance requirements: Requires regular maintenance, such as weed clearing and tree pruning.

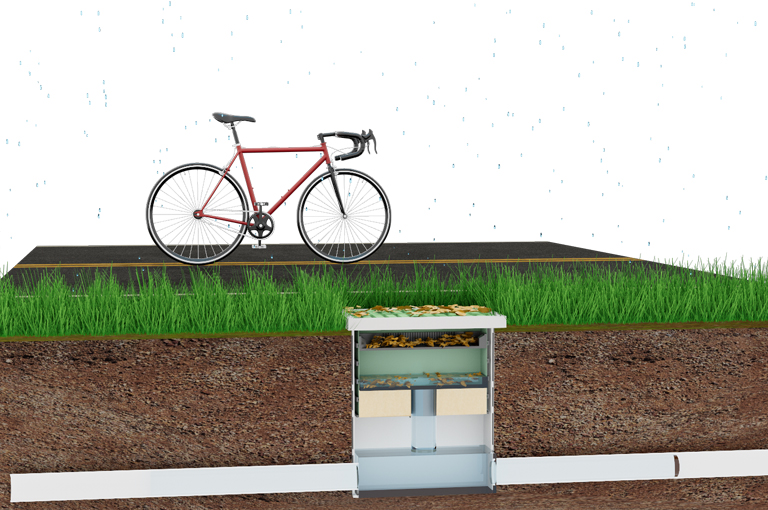
4. Permeable Pavement
Permeable pavement, unlike impermeable surfaces like asphalt or concrete, allows rainwater to infiltrate the soil and groundwater through its porous surface. It aims to promote rainwater infiltration, reduce the burden on urban drainage systems, prevent flooding, and improve the urban environment.
It can:
- Manage stormwater: Promote rainwater infiltration, reducing surface runoff.
- Prevent flooding: Mitigate urban flooding during heavy rains.
- Recharge groundwater: Help rainwater infiltrate, replenishing groundwater resources.
- Environmental cooling: Reduce surface heat accumulation, lowering the urban heat island effect.
Working Principle
- Rainwater infiltration: Rainwater infiltrates through the pores of permeable bricks or pavement.
- Filtration and purification: Filters rainwater pollutants through the gravel layer and soil beneath the pavement.
- Underground drainage: Excess rainwater enters the underground drainage system or naturally infiltrates into the groundwater.
Applications Permeable pavement is widely used in:
- Sidewalks and pedestrian streets: Provides a comfortable walking environment and effectively manages stormwater.
- Parking lots: Reduces surface runoff, prevents water accumulation, and enhances the parking experience.
- Parks and plazas: Used in public green spaces and open areas to enhance landscaping and ecological benefits.
- Residential and commercial areas: Used in neighborhood roads and commercial plazas to improve the environment and manage stormwater.
Advantages
- Eco-friendly and energy-saving: Promotes natural rainwater infiltration, reducing the burden on drainage systems.
- Environmental improvement: Reduces surface water accumulation, lowering the risk of urban flooding.
- Cooling effect: Permeable materials reduce surface temperature, mitigating the heat island effect.
- Easy maintenance: Permeable bricks and pavement are durable and easy to maintain.
Disadvantages
- High initial cost: Materials and construction costs for permeable bricks and pavement are higher.
- Limited load-bearing capacity: Not suitable for heavy traffic roads, only applicable to light load or pedestrian areas.
- Enhanced effect when combined with eco-friendly rainwater inlets.

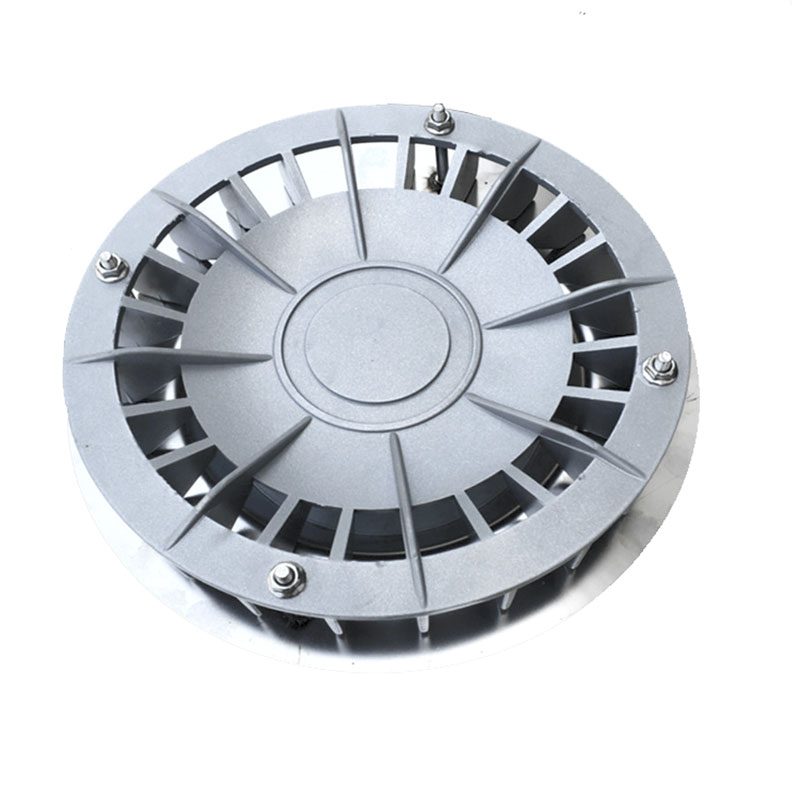
5. Eco-Friendly Rainwater Inlets
Eco-friendly rainwater inlets are innovative stormwater collection devices designed for urban drainage systems. They effectively manage and treat stormwater runoff while minimizing environmental impacts. These inlets usually integrate filtering and purification functions to remove pollutants from rainwater.
It can:
- Collect rainwater: Efficiently collect surface runoff rainwater.
- Purify water quality: Filter pollutants from rainwater, improving discharge quality.
- Prevent clogging: Prevent leaves, debris, and other obstructions from entering the drainage system, reducing blockage risks.
- Reduce flooding: Rapidly drain water, lowering the risk of urban flooding.
Working Principle
- Preliminary filtration: Rainwater passes through a grate or filter mesh at the inlet, intercepting larger debris and trash.
- Sedimentation and purification: Inside the rainwater inlet, sedimentation basins or purification devices further filter fine particles and pollutants from the rainwater.
- Drainage and transport: Purified rainwater is transported through drainage pipes to the underground drainage system or rainwater collection devices.
Applications Eco-friendly rainwater inlets are widely used in:
- Urban roads: Set along the edges of sidewalks and carriageways to efficiently collect and treat road rainwater.
- Parking lots: Installed at parking lot entrances and low-lying areas to prevent water accumulation and pollution.
- Plazas and parks: Used in public green spaces and open areas to enhance stormwater management and landscaping.
- Residential and commercial areas: Used around buildings and low-lying areas to improve the environment and stormwater drainage.
Advantages
- Efficient filtration: Multi-layer filtration systems effectively remove pollutants from rainwater, improving water quality.
- Clog-resistant design: Prevents debris and trash from entering the drainage system, reducing maintenance costs.
- Eco-friendly and energy-saving: Utilizes natural sedimentation and filtration techniques without requiring energy-consuming equipment.
- Easy maintenance: Designed for easy cleaning and maintenance, ensuring long-term effective operation.
Disadvantages
- Regular maintenance requirements: Needs periodic cleaning of filtration devices and sedimentation basins to ensure system functionality.
- Limited application scope: Mainly suitable for light-load areas and public spaces, not for heavy traffic roads.
Eco-friendly rainwater inlets combine eco-friendly and efficient drainage functions, making them suitable for various urban environments and effectively enhancing stormwater management capacity while reducing negative environmental impacts.

6. High-Quality HDPE Water Supply and Drainage Pipes
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are high-quality pipe materials used for water supply and drainage, featuring excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. HDPE pipes are widely used in various water management systems due to their superior performance and eco-friendly characteristics.
Functions
- Water supply systems: Used for transporting drinking water and other domestic water.
- Drainage systems: Used for discharging wastewater, rainwater, and other non-drinking water.
- Industrial applications: Suitable for transporting chemicals, wastewater, and other industrial fluids.
Working Principle HDPE pipes are connected through hot melt welding or electrofusion welding, forming a strong, leak-proof pipe system. Their flexibility and strength allow stable operation under different geological conditions.
Applications HDPE water supply and drainage pipes are widely used in:
- Municipal engineering: Urban water supply and drainage systems, ensuring safe water supply and smooth drainage.
- Building water supply and drainage: Water supply and drainage systems for residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
- Agricultural irrigation: Used for farmland irrigation and drainage, improving agricultural water efficiency.
- Industrial transportation: Used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and other industries for fluid transportation systems.
Advantages
- Corrosion resistance: Excellent resistance to most chemicals, suitable for various environments.
- High strength: Exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, adapting to complex geological conditions.
- Good flexibility: Flexible pipes are easy to install and lay, adapting to ground settlement and temperature changes.
- Leak-proof: Welded connections are leak-proof, ensuring the integrity of the water supply and drainage systems.
- Eco-friendly and safe: Non-toxic and harmless materials, compliant with drinking water transportation standards.
Disadvantages
- High initial cost: Initial investment is higher compared to traditional pipe materials.
- Thermal expansion and contraction: Significant temperature changes require consideration of thermal expansion and contraction during installation.
- Professional installation requirements: Installation requires specialized equipment and techniques to ensure welding quality and system stability.
Choosing the Right BMP Solution
When deciding which BMPs to incorporate into your stormwater solution, consider the following questions:
- What are the climate and weather conditions in the area?
- How much land is available? Is it suitable for construction? Consider factors like topography, soil type, and proximity to other water bodies or drainage areas.
- How much maintenance is required to keep the BMP functioning effectively?
- How will the BMP affect the aesthetics of the property and/or community?
- What impact will the BMP have on the surrounding environment (e.g., water quality, fish and wildlife, insect control, odors)?
Managing stormwater runoff from your facility has no one-size-fits-all solution, so it’s worth considering several different solutions before implementation. The general descriptions of these five stormwater BMPs are just a few of the countless methods for controlling stormwater runoff.
If you have any questions about which stormwater BMP is best suited for your current project, please contact our experts. Our environmental services include:
- Development of Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans (SWPPP)
- Development of Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plans
- Installation, testing, monitoring, and reporting of stormwater systems.